DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14483/22487638.22100Published:
2024-10-27Issue:
Vol. 28 No. 79 (2024): January - MarchSection:
ResearchReconocimiento de Emociones Mediante Región de Ojos Utilizando Características Texturales, lbp y hog
Emotion recognition by eyes region using textural features, lbp and hog
Keywords:
Emotion recognition, regions, textural features, LBP, HoG (en).Keywords:
Reconocimiento de emociones, regiones, Características texturales, LBP, HoG (es).Downloads
Abstract (es)
Objetivo: Nuestro objetivo es desarrollar un sistema robusto de reconocimiento de emociones basado en expresiones faciales, con especial énfasis en dos regiones clave: los ojos y la boca. Este artículo presenta un análisis exhaustivo del reconocimiento de emociones logrado mediante el examen de varias regiones faciales. Las expresiones faciales sirven como indicadores invaluables de las emociones humanas, siendo los ojos y la boca áreas particularmente expresivas. Al centrarnos en estas regiones, nuestro objetivo es capturar con precisión los matices de los estados emocionales.
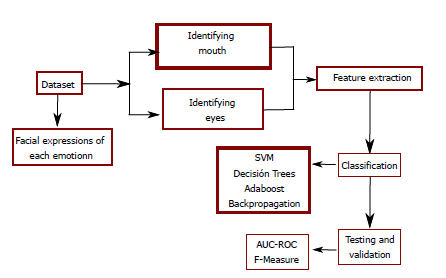
Metodología: El algoritmo que ideamos no solo detecta rasgos faciales, sino que también aísla de forma autónoma las regiones de los ojos y la boca. Para aumentar la precisión de la clasificación, utilizamos varias técnicas de extracción y selección de características. Posteriormente, evaluamos el rendimiento de múltiples clasificadores, incluida la máquina de vectores de soporte (SVM), la regresión logística, la regresión bayesiana y los arboles de decisión, para identificar el enfoque más eficaz.
Resultados: Nuestra metodología experimental implico la utilización de varias técnicas de clasificación para evaluar el rendimiento en diferentes modelos. Entre ellos, SVM exhibió un rendimiento excepcional, con una impresionante tasa de precisión del 99,2 %. Este resultado sobresaliente supero el rendimiento de todos los demás métodos examinados en nuestro estudio. A través de un examen y una experimentación meticulosos, exploramos la eficacia de diferentes regiones faciales para transmitir emociones. Nuestro análisis abarca dos conjuntos de datos y metodologías de evaluación para garantizar una comprensión integral del reconocimiento de emociones.
Conclusiones: Nuestra investigación presenta evidencia convincente de que la región del ojo, cuando se analiza utilizando la máquina de vectores de soporte (SVM) junto con las características de textura, HoG y LBP, logra singularmente una tasa de precisión excepcional del 99,2 %. Este notable hallazgo subraya el importante potencial de priorizar únicamente los ojos para el reconocimiento preciso de las emociones. Al hacerlo, desafía el enfoque convencional de incluir toda el área facial para el análisis.
Abstract (en)
Objective: Our objective is to develop a robust emotion recognition system based on facial expressions, with a particular emphasis on two key regions: the eyes and the mouth. This paper presents a comprehensive analysis of emotion recognition achieved through the examination of various facial regions. Facial expressions serve as invaluable indicators of human emotions, with the eyes and mouth being particularly expressive areas. By focusing on these regions, we aim to accurately capture the nuances of emotional states.
Methodology: The algorithm we devised not only detects facial features but also autonomously isolates the eyes and mouth regions. To boost classification accuracy, we utilized various feature extraction and feature selection techniques. Subsequently, we assessed the performance of multiple classifiers, including Support Vector Machine (SVM), Logistic Regression, Bayesian Regression, and Decision Trees, to identify the most effective approach.
Results: Our experimental methodology involved the utilization of various classification techniques to assess performance across different models. Among these, SVM exhibited exceptional performance, boasting an impressive accuracy rate of 99.2 %. This outstanding result surpassed the performance of all other methods examined in our study. Through meticulous examination and experimentation, we explore the effectiveness of different facial regions in conveying emotions. Ouranalysis encompasses two datasets and evaluation methodologies to ensure a comprehensive understanding of emotion recognition capabilities.
Conclusions: Our investigation presents compelling evidence that the eye region, when analyzed using Support Vector Machine (SVM) along with textural, HoG, and LBP features, singularly achieves an outstanding accuracy rate of 99.2 %. This remarkable finding underscores the significant potential of prioritizing the eyes alone for precise emotion recognition. In doing so, it challenges the conventional approach of including the entire facial area for analysis.
References
Al-Hadithi, B. M.; Cena, C. E. G.; León, R. C. & Loor, C. L. (2016). Desarrollo de un Sistema de Iluminación Artificial Inteligente para Cultivos Protegidos. Revista Iberoamericana de Automática e Informática Industrial RIAI, 13(4), 421-429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.riai.2016.07.005
Ben Amor, B.; Drira, H.; Berretti, S.; Daoudi, M. & Srivastava, A. (2014). 4-D Facial Expression Recognition by Learning Geometric Deformations. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 44(7-8), 2443-2457. https://doi.org/10.1109/tcyb.2014.2308091
Casas, S.; Portalés, C.; Rueda, S. & Fernández, M. (2017). Simulación de Plataformas Robóticas de Movimiento para Aplicaciones de Realidad Virtual Mediante Filtros Digitales. Revista Iberoamericana de Automática e Informática Industrial RIAI, 14(4), 455-466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.riai.2017.07.001
Cervantes, J.; Taltempa, J.; García-Lamont, F.; Castilla, J. S. R.; Rendon, A. Y. & Jalili, L. D. (2017). Análisis Comparativo de las técnicas utilizadas en un Sistema de Reconocimiento de Hojas de Planta. Revista Iberoamericana de Automática e Informática Industrial RIAI, 14(1), 104-114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.riai.2016.09.005
Chakraborty, A.; Konar, A.; Chakraborty, U.& Chatterjee, A. (2009). Emotion Recognition From Facial Expressions and Its Control Using Fuzzy Logic. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics - Part A: Systems and Humans, Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), 39(4), 726-743. https://doi.org/10.1109/tsmca.2009.2014645
Chen, T.; Ju, S.; Yuan, X.; Elhoseny, M.; Ren, F.; Fan, M. & Chen, Z. (2018). Emotion recognition using empirical mode decomposition and approximation entropy. Computers amp; Electrical Engineering, 72(7), 383-392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compeleceng.2018.09.022
Davison, A.; Merghani, W. & Yap, M. (2018). Objective Classes for Micro-Facial Expression Recognition. Journal of Imaging, MDPI AG, 4(10), 119-121. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging4100119
Ekman, P. (1993). Facial expression and emotion. American Psychologist, American Psychological Association (APA), 48(4), 384-392. https://doi.org/10.1037/0003-066x.48.4.384
González, R.; Barrientos, A.; Toapanta, M. & del Cerro, J. (2017). Aplicación de las Máquinas de Soporte Vectorial (SVM) al diagnóstico clínico de la Enfermedad de Párkinson y el Temblor Esencial. Revista Iberoamericana de Automática e Informática Industrial RIAI, 14(4), 394-405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.riai.2017.07.005
He, X. & Zhang, W. (2018). Emotion recognition by assisted learning with convolutional neural networks. Neurocomputing, 291(1), 187-194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2018.02.073
Hossain, M. S. & Muhammad, G. (2019). Emotion recognition using secure edge and cloud computing. Information Sciences, 504(1), 589-601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2019.07.040
Kaur, G.; Sinha, R.; Tiwari, P. K.; Yadav, S. K.; Pandey, P.; Raj, R.; Vashisth, A. & Rakhra, M. (2022). Face mask recognition system using CNN model. Neuroscience Informatics, 2(3), 100035. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuri.2021.100035
Kurbalija, V.; Ivanovi´c, M.; Radovanovi´c, M.; Geler, Z.; Dai, W. & Zhao, W. (2018). Emotion perception and recognition: An exploration of cultural differences and similarities. Cognitive Systems Research, 52(1), 103-116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cogsys.2018.06.009
Liang, Z.; Oba, S. & Ishii, S. (2019). An unsupervised EEG decoding system for human emotion recognition. Neural Networks, 116(1), 257-268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2019.04.003
Li, X.; Hong, X.; Moilanen, A.; Huang, X.; Pfister, T.; Zhao, G. & Pietikainen, M. (2018). Towards Reading Hidden Emotions: A Comparative Study of Spontaneous Micro-Expression Spotting and Recognition Methods. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), 9(4), 563-577. https://doi.org/10.1109/taffc.2017.2667642
Li, X.; Pfister, T.; Huang, X.; Zhao, G. & Pietikainen, M. (2013). A Spontaneous Micro-expression Database: Inducement, collection and baseline. IEEE International Conference and Workshops on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition (FG), IEEE, 1(1), 1-6. https://doi.org/10.1109/fg.2013.6553717
Pfister, T.; Li, X.; Zhao, G. & Pietikainen, M. (2011). Recognising spontaneous facial microexpressions. 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision, IEEE, 1(1), 1449-1456. https://doi.org/10.1109/iccv.2011.6126401
Prasada Rao, K.; Chandra Sekhara Rao, M. & Hemanth Chowdary, N. (2019). An integrated approach to emotion recognition and gender classification. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 60(1), 339-345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvcir.2019.03.002
Sánchez-Alonso, R. E.; Ortega-Moody, J.; González-Barbosa, J.-J. & Reyes-Morales, G. (2017). Uso de Plataformas para el Desarrollo de Aplicaciones Virtuales en el Modelado de Robot Manipuladores. Revista Iberoamericana de Automática e Informática Industrial RIAI, 14(3), 279-287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.riai.2017.04.001
Santhoshkumar, R. & Geetha, M. K. (2019). Deep Learning Approach for Emotion Recognition from Human Body Movements with Feedforward Deep Convolution Neural Networks. Procedia Computer Science, 152(1), 158-165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2019.05.038
Villán, A. F.; Fernández, R. U. & Tejedor, R. C. (2017). Sistema Automático Para la Detección de Distracción y Somnolencia en Conductores por Medio de Características Visuales Robustas. Revista Iberoamericana de Automática e Informática Industrial RIAI, 14(3), 307-328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.riai.2017.05.001
Xiaohua, W.; Muzi, P.; Lijuan, P.; Min, H.; Chunhua, J. & Fuji, R. (2019). Two-level attention with two-stage multi-task learning for facial emotion recognition. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 62(1), 217-225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvcir.2019.05.009
Yap, C. H.; Kendrick, C. & Yap, M. H. (2020). SAMM Long Videos: A Spontaneous Facial Micro- and Macro-Expressions Dataset. Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition, 1(1), 771-776. https://doi.org/10.1109/fg47880.2020.00029
How to Cite
APA
ACM
ACS
ABNT
Chicago
Harvard
IEEE
MLA
Turabian
Vancouver
Download Citation
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Laura Jalili, Josue Espejel, Jair Cervantes, Farid Lamont

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Esta licencia permite a otros remezclar, adaptar y desarrollar su trabajo incluso con fines comerciales, siempre que le den crédito y concedan licencias para sus nuevas creaciones bajo los mismos términos. Esta licencia a menudo se compara con las licencias de software libre y de código abierto “copyleft”. Todos los trabajos nuevos basados en el tuyo tendrán la misma licencia, por lo que cualquier derivado también permitirá el uso comercial. Esta es la licencia utilizada por Wikipedia y se recomienda para materiales que se beneficiarían al incorporar contenido de Wikipedia y proyectos con licencias similares.

