DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14483/23448393.20895Published:
2024-08-04Issue:
Vol. 29 No. 2 (2024): May-AugustSection:
Education in EngineeringScheduling in a Simple Assembly Robotics Cell to Minimize Earliness and Tardiness
Programación de trabajos en una celda robótica de ensamble simple para minimizar los adelantos y las tardanzas
Keywords:
robotic assembly cell, tardiness, scheduling (en).Keywords:
celdas de ensamble robóticas, tardanza, programación (es).Downloads
References
M. P. Groover, "Flexible manufacturing systems," in Automation, Production Systems, and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, Pallavaram, Chennai, India: Pearson Education India, 2016, vol. 4, ch. 16, pp. 460-462.
J. Browne, "Classification of flexible manufacturing systems," The FMS Mag., vol. 2, no. 2, pp. 114-117, 1984. [Online]. Available: https://www.academia.edu/502998/Classification_of_flexible_manufacturing_systems?auto=citations&from=cover_page
H. Gultekin, "Scheduling in flexible robotics manufacturing cells," PhD thesis, Dept. Ind. Eng., Bilkent Universitesi, 2006.
K. K. Abd, "Development of an intelligent methodology for scheduling RFAC," in Intelligent Scheduling of Robotic Flexible Assembly Cells, Berlin, Germany: Springer, 2016, pp. 31-47. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-26296-3_3
T. Sawik, "Simultaneous loading, routing, and assembly plan selection in a flexible assembly system," Mathematical Comp. Model., vol. 28, no. 9, pp. 19-29, 1998. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0895-7177(98)00142-3
G. Levitin, J. Rubinovitz, and B. Shnits, "A genetic algorithm for robotic assembly line balancing," Eur. J. Operational Res., vol. 168, no. 3, pp. 811-825, 2006. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2004.07.030.
K. Abd, K. Abhary, and R. Marian, "Intelligent modeling of scheduling robotic flexible assembly cells using fuzzy logic," 2012. [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/262398812_
M. Pinedo, "Advanced single machine models," in Scheduling; Theory, Algorithms, and Systems, 4th ed., Berlin, Germany: Springer, 2012, ch. 3, pp. 70-77.
K. K. Abd, Intelligent scheduling of robotic flexible assembly cells. Berlin, Germany, Springer, 2015.
A. Jain and H. Elmaraghy, "Production scheduling/rescheduling in flexible manufacturing," Int. J. Prod. Res., vol. 35, no. 1, pp. 281-309, 1997. https://doi.org/10.1080/002075497196082
J. Blazewicz, "Scheduling computer and manufacturing processes," J. Operational Res. Soc., vol. 48, no. 6, art. 659, 1997. https://doi.org/10.1057/palgrave.jors.2600793
R. Ramasesh, "Dynamic job shop scheduling: A survey of simulation research," Omega, vol. 18, no. 1, pp. 43-57, 1990. https://doi.org/10.1016/0305-0483(90)90017-4
C. Koulamas, "The single-machine total tardiness scheduling problem: Review and extensions," Eur. J. Operational Res., vol. 202, no. 1, pp. 1-7, 2010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2009.04.007
J. E. C. Arroyo, R. dos Santos Ottoni, and A. de Paiva Oliveira, "Multi-objective variable neighborhood search algorithms for a single machine scheduling problem with distinct due windows," Electron. Notes Theor. Comput. Sci., vol. 281, pp. 5-19, 2011.
S. French, Sequencing and scheduling. An Introduction to the Mathematics of the Job-Shop. Hemel Hempstead, UK: Ellis Horwood, 1982.
R. L. Graham, E. L. Lawler, J. K. Lenstra, and A. R. Kan, "Optimization and approximation in deterministic sequencing and scheduling: A survey," Ann. Discrete Math., vol. 5, pp. 287-326, 1979. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-5060(08)70356-X
H. Emmons, "One-machine sequencing to minimize certain functions of job tardiness," Oper. Res., vol. 17, no. 4, pp. 701-715, 1969. https://doi.org/10.1287/opre.17.4.701
E. L. Lawler, "A “pseudopolynomial” algorithm for sequencing jobs to minimize total tardiness," Ann. Disc. Math., vol. 1, pp. 331-342, 1977. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-5060(08)70742-8
S. K. Gupta and J. Kyparisis, "Single machine scheduling research," Omega, vol. 15, no. 3, pp. 207-227, 1987. https://doi.org/10.1016/0305-0483(87)90071-5
C. N. Potts and L. N. Van Wassenhove, "A decomposition algorithm for the single machine total tardiness problem," Oper. Res. Lett., vol. 1, no. 5, pp. 177-181, 1982. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-6377(82)90035-9
C.-Y. Lee and J. Y. Choi, "A genetic algorithm for job sequencing problems with distinct due dates and general early-tardy penalty weights," Comp. Oper. Res., vol. 22, no. 8, pp. 857-869, 1995. https://doi.org/10.1016/0305-0548(94)00073-H
B. Yuce et al., "Hybrid genetic bees algorithm applied to single machine scheduling with earliness and tardiness penalties," Comp. Ind. Eng., vol. 113, pp. 842-858, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2017.07.018
J. Rocholl and L. Mönch, "Hybrid algorithms for the earliness–tardiness single-machine multiple orders per job scheduling problem with a common due date," RAIRO-Oper. Res., vol. 52, no. 4-5, pp. 1329-1350, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1051/ro/2018029
H. Kellerer, K. Rustogi, and V. A. Strusevich, "A fast FPTAS for single machine scheduling problem of minimizing total weighted earliness and tardiness about a large common due date," Omega, vol. 90, art. 101992, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omega.2018.11.001
O. A. Arık, "Single machine earliness/tardiness scheduling problem with grey processing times and the grey common due date," Grey Syst. Theory Appl., vol. 11, no. 1, pp. 95-109, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1108/GS-01-2020-0010
W. Wang, "Single-machine due-date assignment scheduling with generalized earliness-tardiness penalties including proportional setup times," J. Appl. Math. Comput., vol. 68, no. 2, pp. 1013-1031, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12190-021-01555-4
How to Cite
APA
ACM
ACS
ABNT
Chicago
Harvard
IEEE
MLA
Turabian
Vancouver
Download Citation
Recibido: 24 de mayo de 2023; Aceptado: 18 de marzo de 2024
Abstract
Background:
Robotics Assembly Cells (RAC) have been designed to meet the f lexibility requirements demanded by today’s globalized market. The objective is to manufacture a vast variety of products at a low cost, which requires equipment with a high level of flexibility, such as robots. The need to schedule a great variety of jobs in an RAC is a very relevant issue, as efficiency and productivity depend on the sequence in which jobs are scheduled. Studies around this matter have developed models with analytical and heuristic approaches, as well as simulation methods and genetic algorithms, seeking to improve performance measures based mainly on time, utilization, and costs.
Method:
The purpose of this article is to formulate an exact mathematical model using mixed-integer linear programming (MILP) to optimize small scheduling problems. The objective is to minimize the measure of performance related to the tardiness and earliness of jobs. This optimization aims to mitigate the effects of delays in product deliveries, queue times, and work-in-process inventory in subsequent processes. Doing so facilitates adherence to agreed-upon delivery deadlines and prevents bottlenecks in the assembly cell.
Results:
The proposed mathematical model generates optimal solutions to the job scheduling problem in the assembly cell, which serves as a case study. This addresses the need to minimize tardiness to meet delivery deadlines or minimize earliness while avoiding an increase in work-in-process inventories. The model ensures that optimal scheduling decisions are made to optimize both delivery performance and inventory levels.
Conclusions:
Due to the NP-hard complexity of the scheduling problem under study, the proposed mathematical model demonstrates computational efficiency in solving scheduling problems with fewer than 20 jobs. The model is designed to handle such smaller-scale problems within a reasonable computational time frame, considering the inherent complexity of the scheduling problem.
Keywords:
robotic assembly cell, tardiness, scheduling.Resumen
Contexto:
Las celdas robóticas de ensamble RAC han sido diseñadas para cumplir con los requerimientos de flexibilidad que exige el mercado globalizado actual. El objetivo es fabricar una alta variedad de productos a bajos costos, por lo cual se requiere de equipos con un alto nivel de f lexibilidad como los robots. La necesidad de programar una amplia variedad de trabajos en una RAC es un problema muy relevante, dado que la eficiencia y la productividad dependen de la secuencia en la cual se programan los trabajos. Los estudios alrededor de este asunto han desarrollado modelos con enfoques analíticos y heurísticos, así como métodos de simulación y algoritmos genéticos, que buscan mejorar medidas de desempeño basadas principalmente en el tiempo, el grado de utilización y el costo.
Método:
El propósito de este artículo es formular un modelo matemático exacto mediante programación lineal entera mixta (MILP) para optimizar problemas pequeños de programación. El objetivo es minimizar las medidas de desempeño de tardanza y adelanto de los trabajos. Esta optimización busca mitigar los efectos de las demoras en las entregas de los productos, los tiempos de cola y los inventarios de producto en proceso en instancias posteriores. Esto permite cumplir con los plazos de entrega pactados y evita bloqueos en la celda de ensamble.
Resultados:
El modelo matemático propuesto genera soluciones óptimas al problema de programación de trabajos en la celda de ensamble propuesta, lo que sirve como caso de estudio. Esto aborda la necesidad de minimizar las tardanzas para cumplir con los plazos de entrega o de minimizar los adelantos y evitar un aumento en los inventarios de producto en proceso. El modelo garantiza que se tomen decisiones óptimas de programación tanto para mejorar los tiempos de entrega como los niveles de inventario.
Conclusiones:
Debido a la complejidad NP-difícil del problema de programación estudiado, el modelo matemático propuesto demuestra eficiencia computacional en la resolución de problemas de programación con menos de 20 trabajos. El modelo está diseñado para manejar tales problemas de menor escala dentro de un marco de tiempo computacional razonable, considerando la complejidad inherente del problema de programación.
Palabras clave:
celdas de ensamble robóticas, tardanza, programación..Introduction
The current market demands increasingly personalized products at mass production prices. This poses a significant challenge for industries worldwide. To remain competitive in a globalized market, industries have implemented flexible manufacturing systems (FMS). FMS allows industries to meet market demands and reduce manufacturing costs, ultimately leading to profitability. FMS offer several advantages, particularly in terms of flexibility, which refers to a system’s ability to manufacture a wide range of products using the same equipment, with short setup times1.FMSaregenerallyclassifiedinto two main subgroups: flexible assembly systems (FAS) and flexible manufacturing systems (FMS) 2. Much of the research conducted in the field has predominantly focused on FMS, while FAS have received comparatively less attention. Both FAS and FMS are categorized as computer-integrated manufacturing systems, but they exhibit distinct differences in several aspects. Firstly, FAS are capable of processing a significantly greater number of diverse tasks compared to FMS. In FAS, multiple components and parts are joined simultaneously, whereas FMS typically operate on one part at a time. Secondly, the processing times required for each operation in FAS are shorter than in FMS. Consequently, the relationship between transfer and processing times in FAS are generally higher in comparison with that of FMS. Thirdly, the material handling systems of FAS tend to be more complex. These differences highlight the uniquecharacteristics and operational variance observed between FAS and FMS, suggesting the need for dedicated research and analysis to understand and optimize the performance of both systems 3. Table I shows some differences between FAS and FMS, which make issues in the former more difficult 4.
Table I: Differences between FAS and FMS

FAS can be classified into two types: robotic assembly lines (RAL) and robotic assembly cells (RAC) (5). A RAL is a line flow system that comprises assembly stations interconnected in series through an automated material handling system. It is primarily employed for assembling products characterized by a high volume and a low variety. These products typically have stable designs and exhibit minimal f luctuations in demand requirements6. TheRACisahighlyadvancedsystemthatincorporatesrobots, assembly stations, and an automated material handling system, all under computerized control. RACs are designed to efficiently assemble a wide range of products in small batches.One of the key advantages of anRACisitsabilitytoutilize one ormorerobotsthatcanperformmultipleoperationssimultaneously or collaboratively. This enables greater flexibility and productivity within the cell 7. Fig. 1 shows the layout of a RAL and a RAC.
Figure 1: Layout of a RAL and a RAC
Scheduling is a decision-making process that plays a vital role in most manufacturing industries. Its function is to optimize the allocation of limited resources for job processing. These resources include machines, robots, tools, material handling equipment, and materials. A job consists of a series of operations or tasks to be performed by manufacturing systems 8. Few studies have addressed the issue of task scheduling in RACs. These studies can be classified into three approaches: the analytical and heuristic approach, the simulation approach, and genetic algorithms. In addition, studies have used different types of performance measures to evaluate the results of scheduling. Measures based on time, utilization, and costs are the most widely used, and time-based performance measures that has attracted the most attention 9. Most of real-life scheduling issues are difficult to solve with a non-deterministic polynomial time NP-hard model and tend to require a large amount of constraints to generate a reliable solution 10.
Scheduling issues in manufacturing systems are specified by a set of elements. The critical elements are decision variables, constraints, and objective functions. The goal of any manufacturing company is to maximize the utilization of resources, minimize completion times, and meet the due dates of orders 11. In field of scheduling, several time-based objective functions are used to evaluate the performance of a system under different scheduling strategies, such as makespan, flow time, tardiness, idle time, queue time, waiting times, and setup times, among others 12. One fundamental aspect when it comes to managing an RAC is to meet the product’s due date, either to deliver the final product to the customer on time or to deliver the semi-finished product to the next process on time, thereby not delaying the system. This job becomes complex when, in a RAC, multiple products with different due dates must be assembled. Here, the problem lies in being able to determine the processing sequence of the tasks that help minimize potential tardiness. Tardiness is defined as the amount of time by which a job exceeds its due date. In scheduling theory, three measures of tardiness are estimated: total tardiness ( Tj), the sum of the tardiness of all late jobs; maximum tardiness (Tmax), the value of the job that obtained the longest tardiness; and the number of tardiness jobs (NT) the amount of jobs that were delivered late 13. The other criterion is earliness, defined as the amount of time by which a job is ahead of its due date. This is a very important and frequent industrial problem that is common to most just-in-time (JIT) production environments. JIT consists of delivering products and services at the right time for immediate use, where the main objective is the continuous search for improving the production process. This is achieved and developed through reduced inventories. JIT scheduling problems are very common in the industry. In a JIT scheduling environment, a job should be finished as close to the due date as possible. An early job completion results in inventory carrying costs, such as those related to storage and insurance 14. Balancing both tardiness and earliness is essential in achieving overall optimization in a RAC. The scheduling algorithm aims to strike a balance between completing jobs within their due dates to avoid tardiness and minimizing excessive earliness to optimize resource utilization. By considering both tardiness and earliness as criteria, manufacturers can effectively manage the assembly process in RACs. Striking the right balance ensures that jobs are completed within the desired time frames, optimizing production efficiency and meeting customer demands without unnecessary delays or excess inventory. Scheduling issues are theoretically classified according to various criteria, such as production volume, the nature of production, production capacity, and manufacturing systems. Each type of scheduling issue has different levels 15,16.
It has been previously mentioned that one of the challenges in scheduling tasks for a RAC is meeting the due dates for an assigned job. In the scheduling area, the tardiness Tj is calculated as the maximum value of the subtraction between the completion time of the job Cj minus the due date Dj 8. This is calculated via Eq. 1:

If job j is finished before the due date, the tardiness is 0, since none was generated. Tardiness does no´t take negative values; if that were to happen, we would be dealing with earliness. On the other hand, the eardiness Ej is calculated as the maximum value of the subtraction between the due date Dj minus the completion time of the job Cj 8. This is calculated via Eq. 2:

It is worth remembering that three measures of earliness are estimated: the total earliness ( Ej), which is the sum of the earliness of all early jobs; the maximum earliness (Emax), which is the value of the job that obtained the maximum earliness; and the number of earliness jobs (NE), which is the amount of jobs that were delivered early.
Scheduling issues for evaluating tardiness and earliness have been solved using heuristic algorithms, exact models, and expert systems 13. The most significant theoretical developments based onheuristic algorithms for the 1||Tj problem are the Emmonsdominanceconditions,knownasEmmons theorems, which determine precedence relationships between jobs to generate an optimal sequence. The f irst Emmons theorem provides the necessary conditions for a shorter job to precede a longer one in an optimal sequence, while the second theorem provides the necessary conditions for a longer job to precede a shorter one in an optimal sequence. These relationships have been extensively used to reduce the solution space in enumeration methods 17. Lawler’s decomposition theorem is the second most significant algorithm. In order to explain the decomposition theorem, let us suppose that the jobs are numbered in the order of the earliest due date or (EDD). According to Lawler 18, the 1||Tj problem is decomposed with the longest j job in a k position. This author makes the following assumption: the longest j job is completed as tardy as possible in an optimal sequence, which means moving the Jobs from left to right while meeting some conditions. The development of these algorithms gave way to several studies, where dispatch rules were defined based on the execution and delivery times of jobs. The most used dispatch rules to solve the aforementioned problem are:
-
First come, first served (FCFS): jobs that arrive first are scheduled first.
-
Earliest Due Date First (EDD): jobs with the earliest due date are scheduled first.
-
Shortest Processing Time (SPT): jobs with the shortest processing time are scheduled first.
-
Longest Processing Time (LPT): jobs with the longest processing time are scheduled first.
-
Slack Time Remaining First (STR): jobs with the minimum slack time remaining are scheduled first. As shown in Eq. 3:

where:
Dj: due date of job j
Pj: processing time of job j
There are many examples where the penalty for a tardiness job remains the same, no matter how long the tardiness is. In this case, the objective is to minimize the number of tardy jobs NT. Moore’s algorithm (1968) minimizes the number of tardy jobs for the problem of a single machine, where all jobs have a same release time. This algorithm consists of four very simple steps. In the first step, the jobs are sequenced while following the EDD rule. Then, the tardiness jobs are ordered according to the LPT rule until an optimal solution is reached 19. Most of the exact algorithms for the 1||Tj problem use the dynamic programming (DP), the branch and bound method (B&B), or a hybrid DP/B&B approach. The most efficient of these algorithms is the Potts and Van Wassenhove (P-W) algorithm, capable of solving problems with up to 100 jobs. The P-W algorithm decomposes the problem until the generated subproblems are small enough to be solved via DP, and it does not use any lower bound 20. The best exact algorithms to solve 1||Tj are the B&B, one that use the latest developments of the Emmons and Lawler decomposition theorems. The performance of these algorithms can be improved by using induced due dates, calculated after certain jobs have been shown to precede/follow others. Szwarc’s branching algorithm (2001) is an example of such algorithm, and it can handle problems with up to 500 jobs. In addition, in the last decade, several algorithms based on metaheuristics and artificial intelligence have been developed to solve tardiness minimization problems, considering more variables and constraints for tasks and machines. These algorithms represent a complex computational development 13.
In the literature, earliness and tardiness penalties are studied by various authors from a single-objective point of view. Most works consider distinct or common due dates.
21 studied the problem considering distinct due dates. They presented an optimal algorithm with polynomial complexity to determine the optimal completion time for each job in a schedule determined byagenetic algorithm (GA). This optimal algorithm wasusedbecauseitmaybeinterestingtoanticipate a job, even paying a penalty if it is shorter than that generated by the tardiness.
22 presented a hybrid genetic-bees algorithm (GBA)-optimized solution for minimizing the weighted sum of earliness and tardiness penalties in the context of the single machine scheduling problem (SMSP). The bee algorithm (BA) was improved by incorporating GA operators during the global search stage, aiming to progressively enhance the BA’s global search capability with new additions.
23 addressed the SMSP while aiming to formulate schedules for tasks with arbitrary due dates and minimizing the total earliness/tardiness with respect to said due dates. The problem was approached through three distinct formulations: 1) where the start time of the machine was fixed, 2) where the start time belonged to a specified time segment, and 3) where the start time was arbitrary. Given the inherent complexity, there is no exact polynomial algorithm for its solution. For the first two formulations, the PSC-algorithms were presented. Each algorithm incorporates clear indicators of feasible solution optimality and is grounded upon optimal solutions for the single machine problem, specifically designed to minimize the total tardiness of tasks relative to their varied due dates with equal weights.
24 addressed the SMSP to minimize the total weighted earliness and tardiness relative to a nonrestrictive common due date. This problem is fundamental and has applications in JIT manufacturing. It is connected to a boolean programming problem with a quadratic objective function, referred to as the half-product. This research presented an approach to create a fast fully polynomial-time approximation scheme (FPTAS) for this problem, and the running time was aligned with the best-known running time for an FPTAS aimed at minimizing a half-product with no additive constant.
25 presented a mixed-integer programming model for a SMSP whose objective was to minimize the total earliness/tardiness duration when the uncertainty of parameters such as processing times and due date was coded with grey numbers. Grey theory and grey numbers serve as tools for representing the uncertainty associated with parameters such as processing times and common due dates. The authors proposed a 0-1 mathematical model to address the problem, coupled with an efficient heuristic method that leveraged the expected processing times for job ordering.
26 studied the SMSP while considering past-sequence-dependent setup times. This study explored scenarios involving common due date assignments, slack due dated, and different due date assignments. The objective function aimed to minimize the linear weighted sum of earliness-tardiness, the count of early and delayed jobs, and due date costs. The optimal properties of the problem were outlined, and it was proven that the problem is solvable in polynomial time. Additionally, three extensions to the problem were proposed: incorporating assumptions of position-dependent, time-dependent, and position-and-time-dependent processing times.
The objective of this article is to develop a MILP model that aids in scheduling and sequencing jobs within a RAC. The aim is to minimize both tardiness and earliness penalties, considering the presence of various job release times. By formulating this new MILP model, this article seeks to generate an optimal solution that surpasses the quality of the results obtained through heuristic approaches and alternative algorithms like the B&B method. This approach offers the advantage of reduced computational complexity. The inclusion of different job release times adds a level of complexity to the problem, which the MILP model aims to effectively address.
Methodology
This study was conducted at the flexible manufacturing laboratory of Facultad de Ciencias Empresariales, Universidad Tecnológica de Pereira. Here there is a RAC called simple assembly robotized cell (SRAC) because it only has one robot. It was designed with the ability to assemble the same family of products, so the robot does not require a gripper change. There are no transfer or setup times, nor trajectory collisions analyzed since the cell is made up of a single robot. Thus, the number of variables is reduced, making it possible to simplify the mathematical model to perform the first tests.
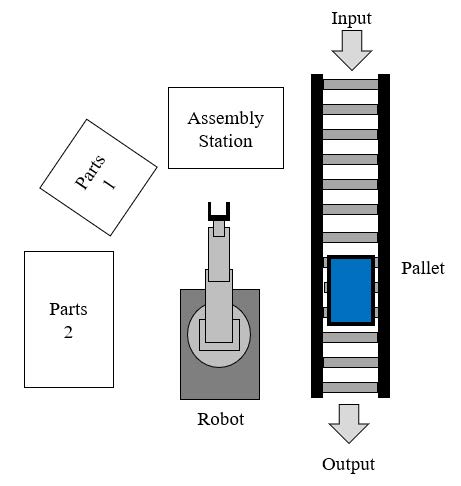
The SRAC is composed of one robot, which takes the components to be assembled from two deposits called Parts 1 and Parts 2. The combination of different parts allows assembling up to 12 different products without the need for reconfiguring of the robot. The task of joining different parts is carried out in the assembly station, and then, when the process complete, the product is positioned on the pallet to be transported to the next stages of the process. SRAC is the first stage of a three-stage process to complete a finished product. Fig. 2 shows a description of the SRAC.
Figure 2: Simple assembly robotic cell (SRAC)
For the first test, the scheduling of 6 jobs was taken as a reference. One job involved a standardized lot of the same product the size of each lot was previously determined to minimize transfer times between jobs. Thus, each time a product needed assembly, all the lot was assembled. Since the SRAC is the first stage in the process, and assuming that the Parts 1 and Parts 2 deposits are always loaded with the required parts, the assembly process does not start until the part from the raw material warehouse arrives at the workstation, which causes job release times to vary. The due dates Dj for the jobs to be assembled at the SRAC were determined through an MRP program that determines due dates according to production orders generated by customer orders. Table II shows the requirements of the jobs to be scheduled in the first run:
Table II: SRAC requirements

Once the information on production requirements was obtained, job scheduling was carried out while following the four dispatch rules described above (FCFS, EDD, SPT, LPT and STR). For the sequencing of the 6 assembly jobs to be processed by the SRAC, there were a total of 6! possible combinations, i.e., 720 different sequencing possibilities. The goal was to find the sequence of jobs that minimizes both earliness and tardiness. An exact mathematical model was formulated, capable of solving the job sequencing problem, with the objective of minimizing the earliness (α) and tardiness (β) penalties. The results obtained with the model were evaluated, validated, and compared against the performance obtained through five dispatch rules.
Development
To formulate the MILP problem, the value of the α and β penalties was taken, which depends on the problem to be addressed. If minimizing the work-in-process (WIP) is required after assembly at the workstation, the value of α must be greater than β. On the contrary, if one wishes to minimize job delays to shorten the makespan of the process, then β must be greater than α. To generate the MILP model, the following variables were defined:
j : subscript that identifies the job to be scheduled
i : subscript that identifies the position in the Schedule
αj : earliness penalties for job j
βj: tardiness penalties for job j
rj: release time for job j
Xij: binary variable, 1 if job j is performed at position i,0 otherwise
Pj: processing time for job j
Ci: completion time for job scheduled at position i
Dj: duedate for job j
Tj : tardiness for job j, no negativity
Ej: earliness for job j, no negativity
Yj: binary variable, 1 if job j has tardiness, 0 else
Zj : binary variable, 1 if job j has earliness, 0 else
Once the job schedules had been obtained by applying heuristic dispatch rules, the following question arose: Is it possible to develop a mathematical model which allows finding a sequence of jobs that minimize the total for earliness and tardiness penalties? The model proposed to answer this question is presented below.
Objective function:

subject to:





Eq. 4 shows the definition of the objective function. Eq. 5 calculates the completion time of the scheduled job at position i. Eq. 6 calculates the earliness or tardiness of job j. If the earliness is greater than zero, the binary variable Zj takes a value of 1, and, if the tardiness is greater than 0, the binary variable Yj takes a value of 1. Eq. 7 establishes that the completion time of job j is greater than the release time plus the processing time when there are different job release times. Eq. 8 determines that a job j can only be scheduled in a single position i . Eq. 10states that, in a position I, only one jobj can be scheduled.
In some cases, the penalty for having an early or tardy job is independent of the time of earliness or tardiness; only having an early or tardy job is penalized. In this case, the objective function is formulated as follows:
Objective function:

Evaluation
To evaluate the proposed MILP model, the performance of the earliness and tardiness penalties was evaluated in relation to the dispatch rules (FCFS, EDD, SPT, LPT, and STR). This section lists, the most important assumptions made in this study:
-
The workstation can perform only one job at a time.
-
Process pre-emption is not allowed.
-
The required sequence of machines and the processing times of the jobs are known.
-
There is no restriction regarding queue length at the workstation.
-
There are no interruptions at the workstation and no machine breakdowns.
-
There are no setup times for jobs.
-
There are no alternate routings.
-
There are no limiting resources other than the workstation.
To evaluate the proposed model, we executed one hundred instances,dividedintothreestages.Here is a summary of the stages and the parameters used.
-
Stage one. Constant penalty values were assumed to analyze the system’s performance when the penalty for tardiness is greater than that for earliness and vice versa. The penalty values used were α =5andβ =10.Inthesecond instance, the penalty values used were α = 10 and β = 5.
-
Stage two. Different penalty values for each job, denoted as αj and βj, were evaluated. These penalty values were generated by drawing data from a uniform distribution with a range of(5-20). This allowed for a more varied and dynamic evaluation of the system.
-
Stage three: Theobjective function was evaluated to minimize the numberoftardyandearlyjobs, considering the penalty values αj and βj generated by the same uniform distribution system in stage two.
The instances of this stage were divided into five groups based on the number of jobs: 6, 10, 15, 18, and 20. For each stage, several parameters were considered to create the instances:
-
Job arrivals. The arrivals of jobs were generated using an exponential distribution.
-
Processing times. The processing times for each job were drawn from a rectangular distribution within the range of (20-100).
-
Due date.Theduedateofeachjobwasdeterminedviaanassignment factor (k),which was randomly selected from a uniform distribution within the range of (2-10).The due date calculation equation was used to determine the specific due date for each job, as shown below.

By varying the penalty values, the number of Jobs and the distribution of job arrivals, process times, and due dates, this study aimed to comprehensively evaluate the proposed model’s performance under different scenarios and conditions. The results obtained for the first 50 instances with constant values of α and β are shown in Table III.
Table III.: Evaluation with α=5;β=10 and α=10;β=5

In this first stage of evaluation, it can be observed that dispatch rules based on delivery deadlines, such as EDD and STR, perform best with responses close to the optimum obtained with the MILP model.These two dispatch rules aim to minimize tardiness, so their performance is better when the value of α is lower tan the value of β. When α is greater tan β , it can be noted that the gap between the two rules and the optimum value increases. Figs.3 and 4 show the comparative curves for the first stage of evaluation.
Figure 3: Performance with α = 5 and β = 10
Figure 4: Performance with α = 10 and β = 5
For the second stage of evaluation, random values of α and β were estimated for each job, as described above. The results obtained are shown in Table IV.
The evaluation shows that when the penalty values α and β are variable and dependent on each job j, the gap between the optimal performance and the analyzed dispatch rules is much larger compared to when constant penalty values α and β were evaluated. This is because the model is able to prioritize jobs based on their penalty values. For example, a job with a high earliness penalty can be scheduled with some tardiness, or vice versa. Furthermore, the model is capable of scheduling jobs in such a way that both earliness and tardiness are equal to zero. This can be achieved by delaying the start of the job, which generates idle time in the assembly cell and allows minimizing the objective function. Fig. 5 provides an example of the described scenario. This analysis demonstrates the flexibility and effectiveness of the MILP model in handling variable penalty values and optimizing the scheduling of jobs to minimize both earliness and tardiness.
Table IV: Evaluation with αj and βj

The SPT rule exhibits a similar performance to EDD and STR, despite not considering delivery deadlines. The performance curves depicted in Fig. 6 provide a visual comparison between the dispatch rules and the MILP model, highlighting their relative performance in terms of minimizing tardiness and earliness penalties. In this figure, it can be observed that the SPT rule achieves a relatively close performance to EDD and STR. SPT prioritizes jobs with shorter processing times, which can indirectly contribute to minimizing earliness and tardiness. While the SPT rule may not explicitly optimize tardiness or earliness, its performance is still competitive, showcasing its effectiveness as a simple and efficient dispatch rule under certain scenarios.
Figure 6: Performance with αj and βj
Finally, in the third stage, the MILP model was evaluated to minimize the penalty for getting a job early or late, regardless of the job’s number of time units spent in tardiness or earliness. For this evaluation, the objective function described in Eq. 10 was taken as a reference. Table V shows the results of the assessment.
No significant differences can be observed between the dispatch rules used, and the gap with respect to the responses obtained by the MILP model increases as more jobs are scheduled. The evaluation results are presented in Fig. 7. It can be seen that, as the number of jobs increases, the performance of the dispatch rules becomes less competitive compared to the optimal solution obtained by the MILP model. This increasing gap highlights the computational superiority of the MILP model in handling larger scheduling problems and achieving more optimal results.
The MILP model demonstrated as significantly superior performance compared to the dispatch rules. However, it should be noted that the computation time of the modelincreases exponentially as the number of jobs increases. The model performs efficiently with a maximum of 20 jobs, but, beyond that, the computation time becomes impractical. Fig. 8 depicts the time curves obtained for the solution of the three types of analysis: constant α and β values, variable αj and βj values, and αjZj andβjYj multiplied by the binary variables. The instances were run on a laptop with an Intel(R) Core (TM) i3-6100U CPU @ 2.30GHz, processor and 6 GB RAM. As expected, the computation time increases as the complexity of the analysis increases, especially when considering variable penalty values and the multiplication of binary variables.
These results highlight the computational limitations of the MILP model and emphasize the importance of considering scalability and computational resources when applying the model to larger scheduling problems. It is crucial to assess the trade-off between computation time and the size of the scheduling problem, in order to ensure a practical implementation. Overall, the MILP model provides excellent performance for small to moderate scheduling problems, delivering optimal solutions within a reasonable computational time frame.
Discussion
The formulated MILP model exhibits limitations regarding the computation time necessary for solving problems with more than 20 jobs. Nonetheless, the model’s application can be instrumental in evaluating the performance of metaheuristic solution techniques. This approach allows determining the gap between the optimal solution obtained with the MILP formulation and that achieved by the proposed algorithm. Consequently, this enables the calibration and scaling of the proposed algorithms to accommodate a larger number of jobs, with an initial comparison conducted on a smaller scale.
Figure 7: Performance with αjZj and βjYj
Figure 8: Computation time to solve MILP model vs. the number of jobs
Following the model evaluation, it became apparent that Eq. 12 significantly contributes to the model’s complexity, thereby increasing computation times. To address this issue, linearizing the calculation is proposed, introducing the variable Si, which determinesthestarttimeofthejobatposition i. This variable is then incorporated into Eq. 13 to calculate the variable Ci. This modification results in an approximately 20% reduction in computation times. While this adjustment improves computational efficiency, its impact is not highly significant, and the formulation remains efficient for up to 20 jobs because, when the number of jobs grows, the number of equations also grows.
The MILP formulation is very efficient when jobs with variable penalty rates are to be scheduled, which generates a program wherethecell incurs a waiting time, so that the jobs do not start before those required to minimize earliness. Undoubtedly, this characteristic considerably improves performance when evaluating the earliness/tardiness of jobs. However, these waiting times can be considered idle and penalize the cell utilization indicator. This opens the possibility of formulating a bio-objective MILP model, where, in addition to minimizing the earliness/tardiness, cell utilization can be maximized, or the makespan can be minimized.
Conclusions
The evaluation results emphasize the importance of utilizing advanced mathematical models (e.g., MILP) for optimizing job scheduling in complex systems. While the dispatch rules may perform well for smaller job sets, their performance deteriorates as the complexity and scale of the problem increase.
The model was developed for an assembly cell with a single robot. We recommend adapting the mathematical model to schedule jobs in assembly cells with more than one robot, analyzing the assignment of tasks to robots, transfer times, and flow shop or parallel systems.
The model is efficient when a reduced number of jobs must be scheduled; if there are more jobs, more computational time will be required to solve the model at an exponential rate
References
License
Copyright (c) 2024 John Andres Muñoz Guevara, Jairo Alberto Villegas-Florez, Jhannier Jhoan Jaramillo Tabima

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
From the edition of the V23N3 of year 2018 forward, the Creative Commons License "Attribution-Non-Commercial - No Derivative Works " is changed to the following:
Attribution - Non-Commercial - Share the same: this license allows others to distribute, remix, retouch, and create from your work in a non-commercial way, as long as they give you credit and license their new creations under the same conditions.











2.jpg)