DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14483/23448350.14958Published:
08/16/2019Issue:
Vol. 36 No. 3 (2019): September-December 2019Section:
Science and EngineeringLaboratorios de informática para mejorar el proceso de cumplimiento fiscal de Colombia
Computer labs to improve Colombia's tax compliance process
Keywords:
digital forensic laboratory, tax evasion, technology (en).Keywords:
evasión fiscal, laboratorio de informática forense (es).Downloads
References
Allingham, M. G.; Sandmo, A. (1972). I Income tax evasion: a theoretical analysis. Journal of Public Economics, 1(3-4), 323-338. https://doi.org/10.1016/0047-2727(72)90010-2.
Alm, J. (1999). Tax compliance and administration. Public Administration and Public Policy, 72, 741-768.
Armas, M. E.; de Eizaga, M. C. (2007). Las nuevas tecnologías en las administraciones tributarias. Télématique: Revista Electrónica de Estudios Telemáticos, 6(3), 84-98.
Avendaño, N. (2005). Evasión en el impuesto a renta de personas naturales: Colombia 1970-1999. Bogotá: Departamento Nacional de Planeación.
Becker, G. S. (1968). Crime and punishment: An economic approach. En The economic dimensions of crime (pp. 13-68). Londres: Palgrave Macmillan. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-349-62853-7_2
Bergman, M. (2003). Tax Reforms and Tax Compliance: The Divergent Paths of Chile and Argentina. Journal of Latin American Studies, 35(3), 593-624. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022216X03006850
Castillo, C.; Romero, A.; Cano, J. (2008). Análisis forense orientado a incidentes en teléfonos celulares GSM: una guía metodológica. En XXXIV Conferencia Latinoamericana de Informática, Centro Latinoamericano de Estudios en Informática (CLEI).
Clotfelter, C. T. (1983). Tax evasion and tax rates: An analysis of individual returns. The Review of Economics and Statistics, 363-373. https://doi.org/10.2307/1924181
Colombia; OCDE (2015). Estudios económicos de la OCDE Colombia. Visión general. Bogotá: OCDE.
Cowell, F. A. (1995). Engañar al Estado: un análisis económico de la evasión. España: Alianza.
Daniel, L. (2011). Digital forensics for legal professionals: understanding digital evidence from the warrant to the courtroom. Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-1-59749-643-8.00003-1
Di Iorio, A. H.; Mollo, M.; Cistoldi, P.; Lamperti, S.; Giaccaglia, M. F.; Malaret, P.; Constanzo, B. (2016). Consideraciones para el diseño de un laboratorio judicial en informática forense. Universidad FASTA. http://redi.ufasta.edu.ar:8080/xmlui/handle/123456789/1564.
Dian (2009). Evasión del Impuesto al Valor Agregado (IVA) en Colombia: 2000-2008. Bogotá: Dian.
Fondo Monetario Internacional (2018). Fiscal Monitor: Capitalizing on Good Times. Washington D.C.: FMI
Franzoni, L. A. (1999). Tax Evasion and Tax Compliance, Italy, University of Bologna. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.137430
Gemmell, N.; Hasseldine, J. (2014). Taxpayers’ Behavioural Responses and Measures of Tax Compliance’ Gaps’: A Critique. Fiscal Studies, 35(3), 275-296. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1475-5890.2014.12031.x.
Gómez Sabaini, J. C.; Jiménez, J. P.; Martner Fanta, R. (2017). Consensos y conflictos en la política tributaria de América Latina. Santiago de Chile: CEPAL. https://doi.org/10.18356/256beeca-es
Hansen, R. S.; Kumar, R.; Shome, D. K. (1994). Dividend policy and corporate monitoring: Evidence from the regulated electric utility industry. Financial Management, 16-22. https://doi.org/10.2307/3666052
Harberger, A. (1987). Modern Developments in Public Finance. Oxford: B. Blackwell.
Hoog, A. (2011). Android forensics: investigation, analysis and mobile security for Google Android. Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-1-59749-651-3.10006-8
Jaimes, L. M. S.; Fuentes, A. S. F. (2013). Metodología para el análisis forense en Linux. Revista Colombiana de Tecnologías de Avanzada (RCTA), 2(20).
Jorratt, M.; Podestá, A. (2010). Análisis comparativo de las metodologías empleadas para la estimación de la evasión en el impuesto a la renta. En: Evasión y equidad en América Latina (pp. 69-94). Santiago: Cepal.
Kahneman, D.; Egan, P. (2011). Thinking, fast and slow (vol. I). Nueva York: Farrar, Straus and Giroux.
Kaplow, L. (2006). On the undesirability of commodity taxation even when income taxation is not optimal. Journal of Public Economics, 90(6-7), 1235-1250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpubeco.2005.07.001
Klepper, S.; Nagin, D. (1989). The deterrent effect of perceived certainty and severity of punishment revisited. Criminology, 27(4), 721-746. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-9125.1989.tb01052.x
Laffer, A. B.; Seymour, J. P. (1981). The economics of the tax revolt: A reader. New York: Harcourt Brace Jovanovich.
López, Ó.; Amaya, H.; León, R; Acosta, B. (2001). Informática forense: generalidades, aspectos técnicos y herramientas. Bogotá: Universidad de los Andes.
Más, F. R.; Rosado, A. D. (2011). La informática forense: el rastro digital del crimen. Derecho y Cambio Social, 8(25), 21.
Mera-Paz, J. A. (2011). Gamificación una estrategia de fortalecimiento en el aprendizaje de la ingeniería de sistemas, experiencia significativa en la Universidad Cooperativa de Colombia sede Popayán. Revista Científica, 3(26), 3-11. https://doi.org/10.14483/23448350.11085
McKemmish, R. (1999). What is forensic computing? Canberra: Australian Institute of Criminology.
Miller, C.; Glendowne, D.; Dampier, D.; Blaylock, K. (2014). Forensicloud: An architecture for digital forensic analysis in the cloud. Journal of Cyber Security, 3, 231-262. https://doi.org/10.13052/jcsm2245-1439.331
Navarro, H. D. B. (2008). Verificación empírica de la curva de Laffer en la economía colombiana (1980-2005). Revista Facultad de Ciencias Económicas: Investigación y Reflexión, 16(1), 151-164.
Organización para la Cooperación y el Desarrollo Económicos (OCDE) (2016). Advanced Analytics for Better Tax Administration. París, Francia: OCDE.
Parra-Jiménez, O. D.; Patiño-Jacinto, R. A. (2010). Evasión de impuestos nacionales en Colombia: año 2001-2009. Revista Facultad de Ciencias Económicas, 18(2). https://doi.org/10.18359/rfce.2279
Paternoster, R. (1987). The deterrent effect of the perceived certainty and severity of punishment: A review of the evidence and issues. Justice Quarterly, 4(2), 173-217. https://doi.org/10.1080/07418828700089271
Plaza-Galvez, L. F. (2016). Obstáculos presentes en Modelación Matemática. Caso Ecuaciones Diferenciales en la formación de Ingenieros. Revista Científica, 2(25), 176-187. https://doi.org/10.14483//udistrital.jour.RC.2016.25.a1
Pollitt, M.; Nance, K.; Hay, B.; Dodge, R. C.; Craiger, P.; Burke, P.; Brubaker, B. (2008). Virtualization and digital forensics: A research and education agenda. Journal of Digital Forensic Practice, 2(2), 62-73. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567280802047135
Rico, C. (1993). La pérdida de recaudo en el impuesto sobre la renta. Aplicación para Colombia: 1978-1992. Maestría en Economía, Pontificia Universidad Javeriana Bogotá, Colombia.
Scholz, J. T.; Lubell, M. (1998). Trust and taxpaying: Testing the heuristic approach to collective action. American Journal of Political Science, 398-417. https://doi.org/10.2307/2991764
Scholz, J. T.; Pinney, N. (1995). Duty, fear, and tax compliance: The heuristic basis of citizenship behavior. American Journal of Political Science, 490-512. https://doi.org/10.2307/2111622
Seco, A.; Muñoz-Miranda, A. (2018). Panorama del uso de las tecnologías y soluciones digitales innovadoras en la política y la gestión fiscal (N.° IDB-DP-00604). Inter-American Development Bank.
Sierra, L. F. H. (2015). Doctrina del Fair Use Prente a los Retos Impuestos por el Entorno Digital-Estudio del Caso Google Books. Rev. Prop. Inmaterial, 20, 57. https://doi.org/10.18601/16571959.n20.04
Slemrod, J.; Yitzhaki, S. (2000). Tax avoidance, evasion and administration. Working Paper w7473. National Bureau of Economic Research. https://doi.org/10.3386/w7473
Toder, E. (2007). What is the tax gap. Tax Notes, 117(4), 367-378.
World Bank (2015). Doing business 2016: measuring regulatory quality and efficiency. Unspecified.
Yun, W. (2005) Foundations of computer forensics: A technology for the fight against computer crime. Elsevier. Computer Forensics. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clsr.2005.02.007
How to Cite
APA
ACM
ACS
ABNT
Chicago
Harvard
IEEE
MLA
Turabian
Vancouver
Download Citation
Recibido: de mayo de 2019; Aceptado: de agosto de 2019
Resumen
El artículo propone el uso de un laboratorio de informática forense regional para ayudar a solucionar el problema de evasión fiscal en Colombia, el cual supone problemas en cubrir las obligaciones públicas del Estado, y lleva a las personas a tener dificultades de consumo y ahorro que afectan la dinámica económica. Pero más allá de las implicaciones normativas, se observa que al implementar nuevas tecnologías en el proceso fiscal para evitar o detectar la evasión se tienen resultados más eficientes. El proceso informático que ayuda a cubrir la evasión fiscal puede mejorarse por medio del análisis de información digital, como lo reflejan los hallazgos de evidencia del uso de laboratorios forenses.
Palabras clave:
evasión fiscal, tecnología, laboratorio de informática forense..Abstract
The paper proposes the use of a digital forensic laboratory to help solve the problem of tax evasion in Colombia that involves problems in covering the public obligations of the State, and leads people to have problems of consumption and savings that affect the economic dynamics, but beyond the normative implications it is observed that when implementing new technologies in the fiscal process to avoid or detect evasion, more efficient results are obtained. The computer process that helps cover tax evasion can be improved through digital analysis as reflected in the findings of evidence of the use of forensic laboratories.
Keywords:
tax evasion, technology, digital forensic laboratory.Resumo
O artigo propõe a utilização de um laboratório forense computacional regional para ajudar a resolver o problema da evasão fiscal na Colômbia, que coloca problemas na cobertura das obrigações públicas do Estado e leva as pessoas a terem dificuldades de consumo e poupança que afetam dinâmica econômica Mas além das implicações normativas, observa-se que ao implementar novas tecnologias no processo fiscal para evitar ou detectar evasão, obtêm-se resultados mais eficientes. O processo computacional que ajuda a cobrir a evasão fiscal pode ser melhorado através da análise de informações digitais, como evidenciado pelas descobertas de evidências do uso de laboratórios forenses.
Palavras-chaves:
evasão fiscal, tecnologia, laboratório de informática forense.Introducción
La evasión y elusión de impuestos se ha considerado como un comportamiento preocupante para todos los gobiernos pues disminuyen recursos fiscales necesarios para el funcionamiento de las instituciones y las políticas públicas. La pérdida de estos recursos puede ser tan grande que se considera gastar grandes sumas de dinero para recuperar alguna proporción de dichos recursos. Este problema se puede resolver de manera más sencilla con la inclusión de la tecnología en la investigación de la evasión de impuestos.
Este tipo de inclusión tecnológica se ha venido dando en los últimos decenios, por el hecho de que cada día se avanza más en herramientas informáticas, de big data y aplicaciones y soportes tecnológicos que hacen más eficientes los procesos. Además, con la ayuda del internet y el almacenamiento en la nube se aprovechan las ventajas de lo que se denomina la era digital; a estas ventajas se debe acceder para mejorar el proceso de recuperación de impuestos.
En este caso en el cual la tecnología disponible abre un abanico de posibilidades de elección, se toma en cuenta la relación costo-beneficio de la implementación de alguna herramienta de estas para el proceso de la determinación e imposición de sanciones que castiguen las prácticas de evasión y elusión de impuestos. Esto significa que no solo se debe ver la forma en que sean más eficientes, sino que cueste menos al Estado, ya que son recursos públicos que por definición son escasos; esto lleva a que se optimicen los recursos, se disminuyan los costos y que tenga los mayores beneficios posibles.
Aquí se plantea que los laboratorios de informática forense regionales serían los más pertinentes en el tema fiscal del país por la relación anteriormente dada, pues permite una descentralización de las herramientas para su uso en varias regiones geográficas sin perder el control de las diligencias de registro, el uso de habilidades y experiencias más eficientes y persuasivas en las diferentes seccionales; además de la capacidad de procesamiento y almacenamiento que presentan, algo que hace más fácil realizar el procedimiento forense.
Revisión de la literatura
Para empezar, hay que entender que los impuestos son incentivos. Es decir, cambian el comportamiento de las personas para sus gastos y para el pago mismo de los impuestos; de esta forma, el pago de impuestos restringe el gasto de las personas al afectar su capacidad de compra y ahorro. Por ello, si los impuestos son muy altos las personas tendrán incentivos para eludirlos porque restringe mucho su capacidad de compra. Este concepto fue aludido en el análisis de la curva de Laffer (Laffer y Seymour, 1981) 1, en el que representan la relación existente entre los ingresos fiscales y las tasas impositivas, donde se plantea que subir la tasa del impuesto no necesariamente aumenta la recaudación pues la base tributaria cae.
De esta forma, en el punto en el que la tasa impositiva es cero, los ingresos fiscales serán nulos, ya que no se aplica ningún impuesto. Mientras que, por el contrario, si la tasa impositiva es del 100 %, los ingresos fiscales también serán nulos, ya que nadie aceptaría producir un bien cuyos ingresos generados fueran destinados en su totalidad a pagar impuestos. Esto permite encontrar un punto de equilibrio en el que la mayor parte posible de personas y empresas pagarán sus impuestos a una tasa que puede ser más baja de la que tienen los países, pero que como más personas la pagan se hace un mayor recaudo.
Además, se sabe que el aumento o tipo de impuesto afecta el precio de los bienes o las rentas (lo cual se llama sustitución real). Por esto, un sistema tributario, que incluye los impuestos y las normas y castigos, da a los individuos incentivos para reducir su pago de impuestos que se considera como evasión de impuestos para no dejar de consumir el bien gravado; es decir, evitar una sustitución real2. De esta forma, se resume las decisiones de los individuos a cumplir o no la normativa y evitar el castigo.
En esta línea hay investigaciones sobre cómo actúan en la evasión de impuestos en un comportamiento de elusión y evasión, así como de los instrumentos de incumplimiento normativo como en Kaplow (2006) y Allingham y Sandmo (1972). En estos estudios se puede ver esta conducta bajo incertidumbre y sobre una que se considera criminal, teniendo en cuenta que la evasión es evitar el pago de los impuestos requeridos y la elusión la disminución de los impuestos que se deben pagar; es decir, minimizarlo dentro del marco legal (Cowell, 1995; Alm, 1999; Franzoni, 1999; Slemrod y Yitzhaki, 2000).
Así es como la evasión de impuestos queda sujeta a los incentivos y al cumplimiento de las normas. Esto es explicado por Becker (1968), quién estudió los determinantes individuales del cumplimiento con las normas tributarias, en donde se define el cumplimiento normativo acorde a la maximización de utilidad de la teoría neoclásica. De este modo, se mira la utilidad personal y la decisión entre uno y varios bienes de consumo o decisiones de pago. Asimismo, los riesgos que perciben los individuos por no cumplir la norma (castigo por no pagar impuestos) (Allingham y Sandmo, 1972; Clotfelter, 1983). de este modo una persona no pagará impuestos si ve poco riesgo de ser castigado y así aumentar su utilidad en la evasión3.
No obstante, ante una falta de maximización de utilidad dejaría atrás la cuantificación racional de los riesgos y pasaría al cálculo de la capacidad de las instituciones para poder darse cuenta de la evasión y la capacidad de castigo real a las personas que no pagan impuestos; esto lleva no solo al análisis individual de la evasión y elusión de impuestos, sino al análisis de las instituciones y su forma de encontrar a los evasores. Ello se puede ver en la teoría de la disuasión descrita por Paternoster (1987) y Klepper y Nagin (1989), que además atañen este análisis a las cuestiones de forma y fondo de las normas y, más importante, la legitimidad de las instituciones.
Esta forma de ver la evasión de impuestos se centra en el cumplimiento de las normas, y se pasa a analizar la forma en que las personas toman decisiones para eludir, evadir o cumplir con dichas normas impositivas. En este sentido, entran a jugar los estudios sobre los costos de oportunidad, las normas sociales y los riegos individuales y colectivos. Esto deja de lado la racionalidad pura y entran otros temas más de la toma de decisiones no racionales4, observando las probabilidades subjetivas del castigo. Ello también centra a la atención en la disuasión en la administración pública tributaria y no solo en el contribuyente, es decir, individuo e institución, mostrando además la importancia de la información que tengan las personas en cuanto al uso de sus impuestos por parte del Estado (Scholz y Pinney, 1995; Scholz y Lubell, 1998).
Otra manera de ver el incumplimiento tributario de personas y empresas fue debatida por Haberger (1987), quien critica la forma como se diseñan los impuestos y la tasa impositiva en sí. Por ejemplo, si hay mayor tasa de impuesto de consumo que de renta la evasión será menor. Sin embargo, investigadores como Bergman (2003) dicen que más allá de la tasa impositiva, a quien se cobra y que tan alta sea, se debe ver cómo las administraciones logran bajar la evasión fiscal siendo más eficientes en el proceso, pasando de la eficiencia del díselo a la eficiencia de la administración tributaria.
Esto último requiere unas instituciones eficientes para que además se envíe una señal a la sociedad de que el incumplimiento de las normas es fácilmente detectable y castigable, si pasa lo contrario cada vez más personas y empresas tendrán incentivos para evadir los pagos. Por tanto, la información cumple un papel importante en la resolución de incentivos de pagos y evasión. Esto se da dentro de la misma institucionalidad, es decir, el ejemplo es una señal muy poderosa para los contribuyentes, ya que se sopesa también el incentivo alto de no pagar y tener más utilidad para el consumo frente al bajo riesgo de castigo.
En el caso específico de las empresas, autores como Slemrod y Yitzhaki (2000) muestran cómo se usa la elusión y los impuestos indirectos que, como ya se dijo, se da dentro del marco legal y logran disminuir la carga impositiva sin modificar la canasta de consumo ni el nivel de producción; es decir, no hay sustitución real. Esto muestra que la forma en que se afecta la tributación y la forma de encontrar y castigar a las empresas puede ser sustancialmente diferente. Una de esas diferencias se puede ver en que la evasión de las personas busca maximizar su utilidad de consumo enfrentando un riesgo de ser castigados, y la elusión de las empresas se hace de forma racional dentro de la norma, es decir, con un grado de elaboración y raciocinio más alto.
Caso colombiano
En el caso colombiano, más allá de la misma aplicación teórica se ve un problema de bajo recaudo, aunque hay suficientes términos impositivos, y en un país en desarrollo es de vital importancia aumentar el recaudo fiscal para soportar el gasto público. En el caso colombiano se recogen ciertos impuestos acordes a los fines de este recaudo, como el impuesto de renta que se usa para la inversión en bienes y capital físico del país como carreteras y el IVA que son para infraestructura como hospitales y escuelas, ello en términos generales. En este sentido, el impuesto que más se evade en Colombia es el IVA según Sierra (2015) que se encontró en alrededor de 4500 empresas que cobran este impuesto y no lo envían a las arcas del Estado, hallándose un incumplimiento en la declaración en el 90 % de ellas.
La Dian se encarga del recaudo de impuestos y la persecución de la evasión y elusión fiscal mediante leyes como la 1819 del 2016, que conforman mecanismos para esta labor enfocándose en la fiscalización y control. Estos mecanismos se describen en el Abecé Reforma Tributaria (2016), donde muestran cómo:
-
fortalecer la Dian: ello en la actualización de la plataforma tecnológica además de nuevos planes de capacitación del personal en fiscalización y control.
-
penalizar la evasión fiscal: la evasión no se consideraba un delito hasta esta reforma, en la que se considera un delito penal evadir el impuesto de renta y el IVA.
-
tipo de pago: se han incluido límites a los gastos en efectivo de las empresas para deducirlos del impuesto de renta y no hagan elusión, llevando a delito estos procedimientos, limitando además en general pagos en efectivo.
-
reforma a mecanismo de control: se intenta controlar de mejor forma los paraísos fiscales con el intercambio de información entre países.
-
régimen sin ánimo de lucro: en este caso se implementa una lista cerrada de actividades que, si merezcan tener beneficios tributarios, evitando que empresas que no lo merezcan usen esta figura como elusión o evasión.
-
la administración tributaria: en este ítem la Dian modifica el régimen sancionatorio generando herramientas que hacen más fácil el cobro y recaudo de impuestos, creando la UGPP (unidad de gestión pensional y para fiscales) que se encarga de la fiscalización de los empleados.
Otro mecanismo usado en la actualidad, en otros países de la región con buenos resultados, es la factura electrónica que deberá ser puesta en marcha en Colombia para todos los contribuyentes. Esta funciona con un sistema informático y una gran base de datos que masifica la facturación y presenta toda la información para el control tributario del país. Esta implementación de nuevas tecnologías se ha dado por los altos niveles de afectación fiscal que repercuten en el déficit fiscal, como lo muestran Parra y Patiño (2010). Esto, además, genera que se deban aumentar los impuestos para cubrir dicho déficit; sin embargo, como ellos mismo plantean se puede generar un problema adicional que consiste en el incentivo a que personas que no evadían impuestos ahora lo hagan ante un aumento cada vez mayor porque los demás no pagan lo que ellos sí.
A ello se suma la evasión de las empresas cuyas modalidades de evasión más observadas, según la Dian (2009), son: a) no declarar los ingresos reales, b) uso del testaferrato a quienes les registran sus activos e ingresos, c) creación de falsas fundaciones sin ánimo de lucro para no pagar impuestos y d) el constante cambio de la razón social de la empresa. Esto podría darse por la carga impositiva que es relativamente alta en el país, y las empresas se ven motivadas a disminuir este pago que es visto como un costo muy alto; empiezan por la elusión de impuestos y, cuando se dan cuenta de que nadie los castiga (falta de eficiencia de entes de control), terminan en la evasión.
Para poder mejorar este horizonte no se debe ver el panorama solo desde las leyes y normas, porque prácticamente castigan todos los delitos fiscales, el problema estaría en la parte operativa en la capacidad de las instituciones. Por ello, se han planteado nuevas formas de trabajar, buscar y castigar la evasión y elusión; en este caso con la inclusión de la tecnología para tal fin, que pretende mejorar la eficiencia de los procesos para poder acelerar y dar mejor soporte a cada caso investigado y para ello se usan cada vez más herramientas informáticas. A continuación, se observará el problema fiscal de la evasión y, posteriormente, se analizará la implantación de estas tecnologías para mejorar los procesos.
Evidencia empírica
Ante la falta de evaluaciones de impacto o evidencia de la implementación de estos programas tecnológicos en la fiscalidad, más específicamente en Colombia, se debe acudir al análisis descriptivo que muestra la relación entre variables macroeconómicas del sistema tributario. Con ello se puede evidenciar el problema que tiene el país para cubrir su creciente gasto, y ante las medidas de incremento de impuestos que se han visto insuficientes y, en muchos casos, como sugiere la teoría y estudios vistos, puede llevar a un problema mayor que afecte la demanda agregada o aumente la evasión. Este último punto lleva a replantear la forma como se debe recaudar y estaría en el sentido de recuperar esta cartera que permite que, por la evasión y elusión fiscal, se pierdan recursos suficientes para cubrir la brecha fiscal, caso que se verá después del análisis descriptivo.
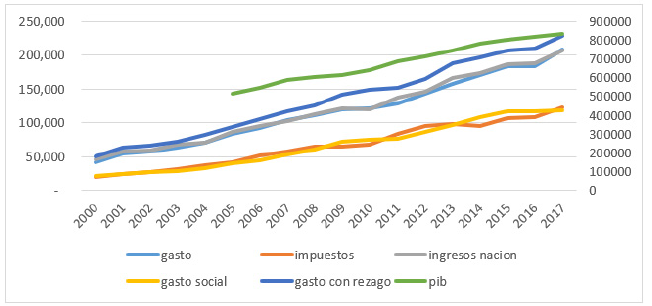
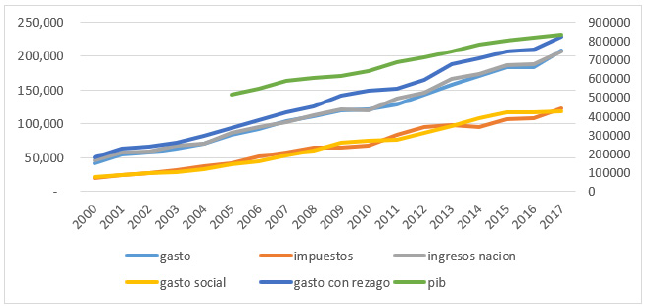
En la figura 1 se puede observar que el gasto con rezago del gobierno ha venido aumentando a un mayor ritmo que los ingresos de la nación, y ambos están alcanzando la senda de crecimiento del producto interno bruto (PIB), es decir, cada vez serán una mayor proporción del PIB. El gasto con rezago es el gasto del gobierno en el tiempo presente más el acumulado (puede ser deuda) de periodos anteriores, ello implica que aunque se pueda cubrir los gastos del gobierno con los ingresos en la actualidad, ya que crecen a un ritmo constante y similar, aún falta cubrir el rezago de los gastos del gobierno y este puede ser cada vez mayor, ya sea por un cambio en el techo de la deuda o por los intereses o riesgos de pago del país, que aun manteniéndose constantes, muestran que necesitan un aumento del gasto para ser sostenibles.
Figura 1: Gasto, recaudo y PIB
Al mirar la composición del gasto que sería en su mayoría proveniente de los impuestos, estos solo cubren el gasto social, es decir, las políticas económicas y sociales guiadas a mejorar el bienestar de las poblaciones, especialmente la más vulnerable. Lo anterior implica que los demás ingresos, como participación en empresas como Ecopetrol, deben cubrir otra gran proporción del gasto, lo que acarrea, además, que se dependa de los precios de los commodities en el mundo, como ocurrió con el descenso del proceso del petróleo de los años 2015 y 2016.
Lo anterior muestra que aunque el recaudo ha venido aumentando, no es lo suficiente para cubrir los gastos crecientes del estado, por lo que es necesario recuperar los impuestos que se pierden por la evasión fiscal para evitar daños a la demanda agregada del país que afecta el producto y la inversión. Esto también significa que, aunque el PIB ha crecido de forma constante, más que todo después del 2009, una proporción más alta del gasto en referencia al PIB debe ser atendida por lo que, si baja el consumo producto de mayores impuestos, afectará en el mediano plazo al PIB y la colocación del gasto. Una muestra más de que se necesita seguir luchando contra la evasión de impuestos.
En la figura 2 se observa la composición de los ingresos por impuestos del Estado. Allí se muestra que el mayor recaudo se hace en la renta y complementarios5, seguido de la retención en la fuente e IVA, lo que carga más que todo al consumo y transacciones comerciales, detrás de ellos esta las declaraciones de IVA6 y, por último, la renta cuotas y retención en la fuente a título de IVA. Estos dos últimos son pagos por cuotas de la renta y la retención es un pago anticipado del IVA. Lo anterior resume el recaudo en dos grandes grupos la renta y el IVA, el primero que es sobre los ingresos de personas o empresas y el segundo sobre el consumo, en suma el de mayor proporción de participación es la renta y ambos impuestos han aumentado de forma similar, lo que implica que el recaudo de los dos ha venido creciendo constantemente; la diferencia entre ellos se da en las reformas tributarias que pueden cargar más a las personas o a las empresas o si es el IVA puede ser más o menos regresivo. Ello implica que la Dian debe enfocarse en ambos impuestos; aunque por eficiencia se pueda recaudar más en el impuesto de la renta, más que todo de mayores o grandes contribuyentes que más allá de las exenciones deben pagar todo el tributo.
Figura 2: Composición de los impuestos IVA y renta.
Evasión fiscal
La evasión fiscal en Colombia presenta ya indicadores preocupantes como lo muestra el informe del World Bank (2015), el cual muestra que el país está en el lugar 136 de 189 en el pago de impuestos, lo que significa que es uno de los países que menos paga sobre la norma vigente, es decir, de los que mayor evasión presenta. Una de las causas que se presentaban era la falta de eficiencia del Gobierno en el recaudo, que en el sistema complejo que tienen de tributación puede afectar a algunas empresas o personas y beneficiar a otras que se aprovechan del sistema o de sus vacíos.
La evasión fiscal en Colombia tiene unos aspectos específicos, más que todo en el contexto internacional, dado el bajo grado de flujos de capital con el extranjero, la evasión del país no responde muchas veces a un fenómeno internacional de paraísos fiscales sino a situaciones internas. Además, es un país con tasas de informalidad bastante altas que son proclives a un sistema de empresas infórmales que no pagan impuesto, lo que genera una especial atención a la evasión de impuestos IVA y Renta por este tipo de estructuras.
Por ello, el país ha presenciado tres reformas tributarias en los últimos 30 años que, según Gómez, Jiménez y Martner (2017), han aumentado el recaudo pasando de un 7,5 % a un 15,1 % desde 1985 a 2014. Es decir, se duplicó el recaudo, aumentando en mayor medida el IVA e impuesto sobre la renta; sin embargo, puede deberse más a los fenómenos económicos propios del mercado que al sistema impositivo, o una mezcla de los dos. Ello, además, permitió que los ingresos de la Dian, que es la entidad que recauda los impuestos, aumentaran un 81 % desde 1985.
Dentro de estos aumentos el de mayor crecimiento fue el IVA, seguido de la actividad externa e impuestos sobre la renta. Sin embargo, también se han presentado aumentos en la evasión de impuestos lo que coloca una potencialidad (metodología explicada en Gemmell y Hasseldine, 2014; Toder, 2007) muy alta del país en el recaudo que se ha visto mermada por este fenómeno. Por ejemplo, según cálculos de la Gómez, Jiménez y Martner (2017), el recaudo potencial ha sido mayor que el efectivo en el país, lo que mostraría una brecha de evasión o elusión fiscal. Según el mismo informe, tres autores realizaron los cálculos con esta metodología (Avendaño, 2005; y Rico, 1993, citados por el autor del informe) quienes mostraron que el monto no recaudado fue de 69 % según (Avendaño, 2005) y 43 % según Rico, 1993), lo que muestra un intervalo de evasión realmente alto.
Un estudio del Hansen, Kumar y Shome (1994) para el Fondo Monetario Internacional (FMI) muestra que la tasa de evasión en Colombia se ubicaba en el 37 % en 1987. Parra y Patiño (2010) mostraron que esta tasa varió (en términos del impuesto del IVA y la renta) del 50 % al 25 % desde la misma fecha; la Jorratt y Podestá (2010) muestran que la evasión en Colombia está entre el 40 % y el 65 %; y la OCDE (2015) que está entre el 25 % y el 30 %.
Las cifras anteriores muestran que la evasión en general en la actualidad se puede ubicar entre el 25 % y el 30 %, y que este ha disminuido desde las mediciones de los años 80, lo que representa una mejora considerable, pero aún se mantiene una preocupación ya que es un porcentaje de evasión alta. Esto abre la puerta a que los mecanismos de recuperación de esos recaudos sean un factor fundamental en el recaudo final de los impuestos; y, para ello, como ya se ha mostrado en esta revisión, es necesario poner en marcha nuevas tecnologías.
Tecnología en el sistema tributario
Los avances tecnológicos han llegado a permear, y lo seguirán haciendo, en los sistemas tributarios. Esto mediante la facilidad que permite para los agentes económicos (Gobierno, personas y empresas) administrar los pagos de los tributos que le corresponden según la norma de cada país; pero, además, se está convirtiendo en una herramienta para evitar la evasión fiscal.
Esta tecnología se basa en el aprovechamiento de las herramientas de las TIC en donde el internet en un eje central que permite administrar todo el tránsito de la información necesario para estos procesos, generando no solo más eficiencia, sino menores costos en todo el sistema (costos para empresas y gastos para las personas). Todo esto optimiza la fiscalización mediante el aprovechamiento de la información, elemento que es central porque no solo evita las asimetrías de la información en la economía que afectan las decisiones de los agentes económicos, si no permite controlar la evasión ya que cualquier caso de evasión o elusión a resolver se debe presentar en términos de la información que se puede volver evidencia. Y, más allá de ello, la información en sí provee la forma de buscar e inducir el pago de quienes evaden, es decir, que la falta de control o la falta de información en la fiscalización en sí es una de las causas de sus problemas en cuanto a la evasión y a los costos del pago.
Al tener un sistema manejado de esta forma hace que los contribuyentes también tengan que pagar menos en la transacción de los impuestos, no porque paguen menos impuestos, sino porque asumen menores costos de transacción y esto incentiva a pagar lo correspondiente si ya de por si hay una mejora previa de su bienestar subjetivo. Esto se ha puesto en funcionamiento en América Latina, especialmente en Chile y Colombia. En el caso de Chile se hace bajo una modificación de las normas y un plan de seguimiento con tecnología de este tipo a la evasión fiscal, además de ello se implementó un sistema con esta tecnología mediante una oficina virtual que controla todos los trámites administrativos, permitiendo la eficiencia en el proceso y menores costos a los contribuyentes7 (Armas y de Eizaga, 2007).
Según Armas y de Eizaga (2007), la Dian en Colombia creó un modelo único de ingresos, servicio y control automatizado (Muisca), que tenía como objetivo principal la recaudación más eficiente de los impuestos, pero también el control sobre los pagos, es decir, una forma de seguimiento para evitar la evasión. Sin embargo, este sistema se desarrolló para hacer más eficientes los procesos mediante una metodología de estandarización de documentos, recolección y almacenamiento de datos.
Esta evolución de la tecnología en la tributación se está dando a nivel mundial como lo muestra la OCDE (2016) quienes emitieron una serie de recomendaciones para su uso, esto es en mayor medida para evitar la evasión fiscal, con la premisa de nuevo de mejorar la información más que todo para evitar que se fuguen capitales a paraísos fiscales, por lo que la cooperación internacional en este caso es vital. Entonces, el primer paso para evitar problemas de evasión es mejorar la información, esto en los problemas internos de cada país y en los externos fiscalización internacional; esta mejora en la información se da con nuevas tecnologías de información.
Según las cifras de la OCDE, desde 2014 estas herramientas permitieron recaudar más en los países miembros (Colombia entró en el 2018, y tendrá que ajustarse a estas recomendaciones), con una herramienta de acceso a la información y el intercambio de esta. Como se ha mencionado, comenzó como una herramienta de control internacional que ha permitido al fisco recuperar, según la OCDE, hasta 85 000 millones de dólares.
En esta misma línea el FMI (2018) mostró que la inclusión de tecnologías digitales en la política fiscal permite reducir la evasión de impuestos. Además, expone cómo con las bases de datos digitales se detecta más fácilmente comportamientos que pueden ser de fraude fiscal. Según sus estimaciones, estas herramientas digitales permitirán aumentar la recaudación entre el 1 % y el 2 % del producto interno bruto (PIB).
Estos informes de nuevo consideran que el mayor problema es, en la evasión internacional, con los paraísos fiscales, por lo que también recomiendan que una vez se obtenga más información esta sea compartida entre países socios o por convenios fiscales internacionales, puesto que la evasión interna puede volverse externa en cualquier momento se deben combatir los dos frentes. Asimismo, afirman que no solo se debe aplicar medidas a la tecnología para la evasión sino para facilitar el pago de impuestos, ya que muchas personas o empresas pequeñas no tienen claro que deben pagar ni cómo hacerlo, ello desde herramientas como internet, con celulares o diferentes plataformas que ya se usan mundialmente.
Por último, el informe aclara una de las cuestiones más problemáticas del uso de herramientas digitales, por un lado la desconfianza en los gobiernos que no se puede controlar en esta fiscalización, porque es un problema de democracia; y, por otro lado, los fraudes por medios digitales son cada día mayores, por ello aunque se avance en la digitalización de los procesos estos deben tener un control minucioso y una seguridad muy alta ya que un fraude digital puede llegar a ser mucho más grande que los que se daban antes.
Por otro lado, el informe de la OCDE (2016) propone una serie de herramientas para la digitalización fiscal que se resumen en una supresión de las ventas electrónicas y contra-tecnología, la falsa facturación, la circulación excesiva de efectivo y malas prácticas fiscales.
Implementación de la tecnología en la fiscalidad
La decisión de aplicar estas herramientas informáticas es de política pública, en particular para mejorar las políticas fiscales, es decir, mejorar el funcionamiento de la Dian. El desarrollo de nuevas tecnologías intensifica el trabajo en los bienes intangibles y en la acumulación de la información, por ejemplo, al centrarla y descentralizarla, o mejor dicho en la forma de adquirir más información de las regiones más alejadas del centro o polo informativo e informático que en el caso de Colombia la central está en Bogotá.
Esto implica, además, que dentro de la mayor productividad que puede generar poner en marcha estas tecnologías está el mejor funcionamiento y el menor costo, lo que acarrea que cada nuevo avance debe representar una ventaja en términos de costo-beneficio. Según los cálculos del informe de la OCDE, en países como Austria se espera recaudar 900 millones de euros adicionales por el uso de estas herramientas informáticas, en Bélgica el aumento de un 8 % y en Canadá una cifra cercana al 1,2 billones de dólares; lo anterior evaluando programas de facturación electrónica e intervención vía digital en el sector turismo de estos países.
En cuanto al cálculo del IVA en los países estudiados, se encontró que el recaudo aumentó un 15 %, superando con esta cifra los costos de la implantación de los programas de innovación tecnológica para la recaudación y evasión de impuestos. Por ejemplo, en Suecia se han conectado desde el año 2010 135 000 cajas registradoras con la unidad de control fiscal, permitiendo que se incluyan las transacciones en efectivo, y la recuperación de IVA y otros impuestos fue de 300 millones de euros.
Ello permitió ver, además de los resultados fiscales, que las empresas se beneficiaron porque evitaron en mayor medida los robos por parte de los empleados de las empresas que se aprovechaban de los vacíos en la información contable, lo que en términos económicos es una externalidad positiva de las nuevas tecnologías en la fiscalidad. También, con estas herramientas se reduce el tiempo en las intervenciones para la evasión de impuestos, por ejemplo, en Quebec el tiempo se redujo de 70 a 3 horas y se centraliza la información necesaria para su uso de intervención, de búsqueda de evasión y de legislación para procesos penales.
Por otro lado, uno de los temas que más impacto puede tener y que se estudia en la actualidad es la factura electrónica. La comisión la muestra como una buena herramienta ya que permite conservar los registros de las transacciones con los clientes y obligatoriamente dan factura a los mismos, el sistema central toma la información para su estudio o registro, ello debe respaldarse con firmas electrónicas para evitar fraudes para la empresa y el gobierno. Esta herramienta necesitaría de la comparación de los datos del vendedor y el comprador ya sea de forma periódica o al instante.
En Colombia esto ya se ha hecho con buenos resultados, y también en otros países de la región como Argentina, Bolivia, Brasil, Costa Rica, Ecuador, Guatemala, Perú y Uruguay (Seco y Muñoz, 2018). Y solo en México se ha evaluado de forma más profunda y se proyecta que 4,2 millones de microempresas llegarán a la economía formal, mostrando otra externalidad positiva, esta vez en la formalidad de la económica.
Laboratorios de informática forense regionales
Este estudio parte del análisis de la informática forense, conocido como una ciencia que parte de conceptos y procedimientos de las ciencias forenses. La informática forense tiene como objetivo replicar los métodos de la ciencia forense en general, enfocándose hacia el análisis de datos y, lo más importante, la evidencia digital. Todo ello en plataformas tecnológicas que soporten el almacenamiento y procesamiento de la información y grandes datos.
Antes de ahondar en el tema, es necesario mostrar que este tipo de análisis forense digital ha comenzado a usarse en varias ciencias y aplicaciones, sobre todo de seguridad. Esto trae consigo que ha sido probado su uso en ámbitos de seguridad informática y su eficiencia ha permitido desarrollar mejores procesos; esto se observa en Jaimes y Fuentes (2013), quienes demuestran la operatividad en plataformas informáticas para el análisis forense.
Además, se puede observar su aplicación en Hoog (2011) y Daniel (2012), quienes muestran la aplicación del análisis forense digital en dispositivos móviles, más que todo en la confiabilidad de la información para las empresas y los usuarios; y en otro tipo de crímenes, como se ve en Mas y Rosado (2011), quienes muestran sus aplicaciones forenses en general, además de las ventajas de los rastros digitales que son únicamente vistos con un análisis forense digital. Y, como se ha dicho, esto se aplica mejor en un laboratorio que lo permita. La validez de este tipo de procedimientos se ha avanzado en diferentes sistemas operativos, uno de los más estudiados es Linux. Según Jaimes y Fuentes (2013), que muestra la verificación y eficacia de este sistema que sigue vigente a pesar de los avances tecnológicos. A esto llega la computación forense explicada por Wang et al. (2005), quienes muestran que llega ante la evolución de la era digital que va más allá de la seguridad informática y toma el papel de seguidor y rastreador para la conformación de evidencia forense, que no se dan solo en delitos informáticos sino se puede llevar a más ramas.
En la experiencia particular, se ha evidenciado que en Colombia se tienen más preferencias por los sistemas operativos licenciados o software propietarios, debido incluso a que no existen políticas gubernamentales de uso de software libre. Por lo que crecemos en un entorno en el que todo tiene software Propietario: en el colegio, en la universidad, en la empresa, en el trabajo, en las entidades estatales, bancos, entre otros.
Esto permite ahora centrarse en la evidencia digital que se encuentre involucrada en una investigación o indagación, como recopilación, preservación, análisis y reportes de la prueba digital. Ello, como los demás análisis forenses, parten a tomar una estructura de evidencia legal para formar un caso o soportar uno abierto. Por ello, cada evidencia digital debe ser presentada bajo resguardo legal y sometida a otras pruebas de fidelidad como las demás evidencias.
Esto lo explican Castillo, Romero y Cano (2008) y McKemmish (1999), para quienes al llevar ese proceso se debe hacer de manera confiable y que sea legalmente válido. Para ello, se necesita prueba digital de dos maneras: a) la primera es ver la evidencia digital como una prueba ordinaria y b) se debe considerar como evidencia no latente, es decir, que se trate en un marco legal legítimo para la recolección y preservación de esta.
Las pruebas digitales se recolectan, trasladan, analizan y almacenan según sea el caso particular y deben garantizar la reserva e integridad de su información, procesos que deben ser ajustados a un patrón o tipo común por las entidades que las requieren, mostrando la custodia de la misma y registrando la manipulación de cada una para que las conclusiones de estas sean fácilmente repetibles y auditables.
Para todo este proceso es necesario que estas pruebas tengan una función orientadora en la que da un hilo conductor sobre los hechos y una función probatoria donde la evidencia se puede mostrar en un proceso. De esta forma, se considera prueba digital a la información que está sujeta a manipulación humana, electrónica o informática y ha sido extraída de un medio tecnológico. Esta se presenta en medios físicos, pero presenta diferencia con la evidencia física, puesto que es intangible, puede duplicarse las veces requeridas o necesarias y son copias idénticas a la original, además no puede modificarse fácilmente por lo que debe ser protegida más estrictamente (Di Iorio et al., 2016).
Las pruebas digitales tienen que ser analizadas y procesadas para sacarles el máximo provecho, la creación de caso y el posterior aporte de pruebas digital requiere infraestructura tecnológica adecuada para la consecución de las pruebas que permitirán la imputación de los delitos identificados. Ahora bien, es necesario comparar el desempeño de un sistema físico frente a uno virtual. Entonces, se presentan dos escenarios: uno físico en donde cada institución tiene un “mini” laboratorio forense y otro en el que existe un laboratorio macro y desde cada institución realizan acceso remoto al mismo y cargan o descargan información en un entorno virtualizado.
Al ver la necesidad y utilidad del análisis forense informático, es necesario observar las ventajas de un sistema central digital que responda a las necesidades como almacenamiento y procesamiento de tal cantidad de datos. Esto lo plantea más específicamente Craiger, Burke, Marberry y Pollitt (2008), quienes afirman que este proceso es ineficiente en laboratorios descentralizados, esto implica un gasto monetario mayor por los equipos e instalaciones en cada sede, además que la falta de capacitación de algunas personas, algo que no siempre se controla, puede dañar la cadena de custodia o la evidencia en sí. Para ello se plantea que los laboratorios en el futuro serán virtuales, esto involucra cortar las barreras geográficas.
Ahora bien, es importante tener en cuenta los cuidados que los funcionarios deben tener al recolectar la evidencia que en un futuro será el material probatorio para iniciar cualquier proceso de corrección, determinación e imposición de sanciones a los contribuyentes con irregularidades en sus procesos. El perfilamiento, la recolección, el procesamiento y la conservación de las evidencias hace parte del proceso de recolección de pruebas, el análisis y el informe final que determina los valores a corregir de existir diferencias en lo declarado y la realidad económica del contribuyente.
Al descentralizar las herramientas con un entorno virtualizado se da el acceso a los funcionarios desde cada seccional, permitiendo incluso controlar el acceso a cada caso y verificando el avance de los que están en curso. Esta descentralización proporciona más seguridad ya que incorpora una red de área de almacenamiento y virtualización tecnológica, se reduce la duplicidad de recursos y tareas disminuyendo los costos y la pérdida de información por inexperiencia, y uno de los aspectos más pertinentes que da la ventaja a estos sistemas en la capacidad de procesar una cantidad de datos mayor a través de internet, reduciendo el tiempo de procesamiento de las pruebas digitales llevando las mismas herramientas a varios sitios y grupos con la misma eficiencia o superior que un laboratorio físico y a menor costo (Miller, Glendowne, Dampier y Blaylock, 2014).
De esta forma, la propuesta de laboratorio digital permite la identificación, recolección y procedimiento de la información contenida en los dispositivos de almacenamiento digital, con lo cual se determina un proceso de recolección, tratamiento y análisis de dicha información para detectar las posibles evasiones fiscales. Así, se puede seguir una serie de pasos en los que el laboratorio forense digital hace que el proceso sea más eficiente para enfrentar la evasión fiscal.
En primer lugar, se realiza un perfilamiento de la organización en la que se realiza el análisis de la coyuntura de la intervención en la vistita a las empresas los análisis del perfil del contribuyente. En este sentido, la información del perfilamiento puede ser igualmente almacenada y de fácil acceso con un laboratorio digital en la cual todos acceden de forma remota a dicha información; si son seccionales podrían ingresar a la base de datos central sin necesidad de más usos tecnológicos, lo que permite que se hagan procedimientos en más puntos geográficos.
Por otra parte, se realiza un registro del procedimiento que integra la proposición de objetivos, el desarrollo y registro de las actividades. Ello requiere el registro de toda la logística de personal y equipos que van a ser usados; de nuevo, esta información puede ser almacenada y usada por varias oficinas en varios procedimientos y retroalimentar los formatos para el diligenciamiento de los procedimientos. Después del registro los funcionarios realizan el trabajo de verificación de la información y de los soportes documentales (digitales) del procedimiento, examinando aquellos que pueden ser potencialmente evidencia digital para ser analizados en el laboratorio con cifrado informático o se consideren de este tipo, que incluye datos, textos, imágenes; y dentro de la evidencia digital se recolectan dispositivos de almacenamiento que puede considerarse archivos o fuentes de archivos digitales o imágenes.
Estas imágenes se obtienen de forma física o lógica. En la física se obtiene un archivo de imagen con la totalidad de la información dentro del dispositivo de almacenamiento; en la lógica se obtiene una imagen de una fracción de la información contenida o de varias fracciones. Estos archivos se autentican mediante un sistema de verificación probado (hash, y se debe tener especial cuidado con la integridad de esta evidencia para que los procesos fiscales sean válidos. La capacidad de procesamiento y adaptación de los laboratorios digitales permiten que se dé un mejor tratamiento a la prueba digital en todas las zonas geográficas donde se actúa, además de la facilidad de obtención de la información de un proceso y de modificación de los procedimientos para hacerlos más eficientes.
Asimismo, el laboratorio digital adquiere relevancia en la supervisión de los procedimientos para que la prueba digital sea pertinente a la investigación, esto por el acceso rápido y seguro a la información y procedimientos que se tiene en cualquier momento. Adicional a esto, garantiza una posible repetición y auditoría de la información para verificar la viabilidad y pertinencia operativa y legal, es decir, que sea más eficiente en la preservación y consolidación de la información y análisis dado.
Este análisis de las imágenes o archivos forenses (digitales), realizados en el laboratorio forense digital, permite identificar fácilmente los elementos relevantes de cada caso, mediante el uso de las técnicas informáticas y de datos, para obtener o identificar los archivos, bases de datos, hojas de cálculo, documentos, correos electrónicos, archivos contables, facturación, entro otros, que pueden demostrar una evasión fiscal. Después de este procedimiento, el laboratorio digital permite que la información, los archivos y evidencias puedan ser ubicados en dispositivos cifrados para la consolidación de la información, lo cual genera una visualización y posible análisis de los archivos de forma fácil y rápida por parte de cualquier funcionario capacitado y que tenga estas funciones.
Finalmente, con un entrono virtualizado para la ejecución de las labores propias de auditoría entre las seccionales, se brindan la mayor parte de herramientas de las que dispone el nivel central beneficiando en primera medida la agilidad y prontitud con la que se realizan los informes de auditoría y el aporte de pruebas de este, permitiendo que se puedan sustanciar los procesos más ágilmente y no se dependa tanto de la disponibilidad de recursos físicos centralizados.
Conclusiones
El sistema tributario en Colombia presenta problemas de recaudo que no permiten tener un balance fiscal favorable para el país, generando un pasivo y una deuda muy alta para el estado, ello involucra que se deba cubrir con mayores ingresos tributario. Estos ingresos provienen de las empresas y personas que pagan los impuestos, pero ante tasas impositivas cada vez mayores no se han tenido los resultados esperados porque hay un problema de evasión y elusión de impuestos en el país que hace que las personas que pagan impuestos sigan cubriendo este hueco fiscal y terminaran evadiendo impuestos si se afecta mucho su consumo.
La normativa que castiga la evasión de impuesto es amplia y está bien definida en cada modalidad de evasión o elusión. Esto acarrea que el castigo por evadir impuestos ya está dado y legalmente se tienen unos procedimientos establecidos para dicha tarea. Es decir, no es el caso de la falta de normas o de incentivos y castigos para solucionar el problema lo que hace falta en el país, sino mejorar los mecanismos para optimizar los procesos internos de este trabajo.
Lo anterior implica darle más herramientas a las zonas más alejadas de los centros donde trabaja nórmamele la Dian, es decir, en las grandes ciudades, ya que las empresas aunque se concentran en ciertos centros urbanos, tienen sedes o sitios donde producen los bienes y servicios a los cuales estas sedes centrales no pueden acceder fácilmente, no solo en el orden físico, sino logístico del mismo procedimiento, y a veces es más costoso adquirir las herramientas y habilidades para estas zonas que lo que se logra recaudar.
Por esto, los laboratorios forenses digitales dan dos tipos de ventajas para trabajar de forma descentralizada, pero a la vez con control centralizado, esto significa que dichos laboratorios dan las herramientas a los funcionarios de la Dian en todo el país para que puedan procesar los datos o evidencias de sus procesos y lo hagan mediante el acceso a unas máquinas virtuales con procesadores mucho más potentes que los recursos de una seccional. Esto permitiría que el proceso sea mucho más capaz y rápido, pues este acceso remoto desde cualquier parte del país a la base central admite que las herramientas estén disponibles para todo aquel que las necesite en sus procesos. Pero, además, permite un centro centralizado de todos los procesos, ya que toda la información que sea usada queda almacenada al instante en la base central de la Dian, que tendrá acceso a dicha información para su control.
El control de los recursos dispuestos para ser utilizados por los funcionarios de las diferentes seccionales debe estar en el nivel central en donde se controla el acceso a la información, así se administra su uso garantizando la reserva de los archivos almacenados garantizando un acceso ágil y eficiente de cada uno de los auditores.
Por último, todo esto ayudaría a combatir la corrupción en los funcionarios ya que al tener acceso en tiempo real a todos los procesos en el país es posible hacerles un mejor seguimiento que con herramientas no digitales que deben trasladarse en físico y esperar que externamente se generen informes o información que se necesita. Por estas ventajas es recomendable implementar los laboratorios forenses digitales en el proceso que realiza la Dian para evitar la evasión fiscal.
Referencias
License
Copyright (c) 2019 Fabián Giovanni González-Robayo, Juan Sebastián González-Sanabria, Lucero Tellez-Hernandez

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
When submitting their article to the Scientific Journal, the author(s) certifies that their manuscript has not been, nor will it be, presented or published in any other scientific journal.
Within the editorial policies established for the Scientific Journal, costs are not established at any stage of the editorial process, the submission of articles, the editing, publication and subsequent downloading of the contents is free of charge, since the journal is a non-profit academic publication. profit.