DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14483/23448393.21311Published:
2024-07-17Issue:
Vol. 29 No. 2 (2024): May-AugustSection:
Biomedical EngineeringA Comparative Analysis between FFT, EMD, and EEMD for Epilepsy Detection
Análisis comparativo entre FFT, EMD y EEMD para la detección de epilepsia
Keywords:
electroencephalogram, Empirical Mode Decomposition, epilepsy, Instantaneous Frequency, Intrinsec Mode Functions, methodology, non-lineal, non-stationary, oscillation modes, seizures (en).Keywords:
convulsiones, Descomposicion Empírica de Modos, electroencefalograma, epilepsia, Frecuencias Instantáneas, Funciones de Modo Intrínseco, metodología, modos de oscilación, no-estacionaria, no-lineal (es).Downloads
References
R. S. Fisher et al., "Ilae official report: a practical clinical definition of epilepsy," Epilepsia, vol. 55, no. 4, pp. 475-482, 2014. https://doi.org/10.1111/epi.12550
A. T. Tzallas et al., "Automated epileptic seizure detection methods: a review study," Epilepsy-Histol. Electroencephalogr. Psychol. Asp., pp. 2027-2036, 2012. https://doi.org/10.5772/31597
K. M. Fiest et al., "Prevalence and incidence of epilepsy: a systematic review and meta-analysis of international studies," Neurology, vol. 88, no. 3, pp. 296-303, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000003509
S. Roy, I. Kiral-Kornek, and S. Harrer, "A deep recurrent neural network for abnormal eeg identification," in Proc. 17th Conf. Artif. Intell. Med (AIME), Poznan, Poland, Jun 26-29, 2019, pp. 47-56. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-21642-9_8
L.-D. Guerrero, L. D. Romero, and M. Bueno-Lopez, "A review of epileptic seizure detection using eeg signals analysis in the time and frequency domain," in 2021 IEEE 21st Int. Conf. Commun. Technol. (ICCT), 2021, pp. 1363-1367. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCT52962.2021.9657835
O. Karabiber Cura, S. Kocaaslan Atli, H. S. Ture, and A. Akan, "Epileptic seizure classifications using empirical mode decomposition and its derivative," Biomed. eng., vol. 19, pp. 1-22, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12938-020-0754-y
P. A. Munoz, E. Giraldo, M. B. Lopez, and M. Molinas, "Automatic selection of frequency bands for electroencephalographic source localization," in Proc. 2019 9th Int. IEEE/EMBS Conf. on Neural Eng. (NER), 2019, pp. 1179-1182. https://doi.org/10.1109/NER.2019.8716979
J. Engel Jr, "Evolution of concepts in epilepsy surgery," Epileptic Disorders, vol. 21, no. 5, pp. 391-409, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1684/epd.2019.1091
E. Ceballos Dominguez, M. Subathra, N. Sairamya, and S. Thomas George, "Detection of focal epilepsy in brain maps through a novel pattern recognition technique," Neur. Comput. and Appl., vol. 32, pp. 10 143-10 157, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-019-04544-8
N. van Klink et al., "Simultaneous meg and eeg to detect ripples in people with focal epilepsy," Clin. Neuroph., vol. 130, no. 7, pp. 1175-1183, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2019.01.027
G. Zazzaro, S. Cuomo, A. Martone, R. V. Montaquila, G. Toraldo, and L. Pavone, "Eeg signal analysis for epileptic seizures detection by applying data mining techniques," IoT, vol. 14, p. 100048, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iot.2019.03.002
S. Kulaseharan, A. Aminpour, M. Ebrahimi, and E. Widjaja, "Identifying lesions in paediatric epilepsy using morphometric and textural analysis of magnetic resonance images," NeuroImage: Clinical, vol. 21, p. 101663, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2019.101663
L. A. Moctezuma and M. Molinas, "Eeg channel-selection method for epileptic-seizure classification based on multi-objective optimization," Front. Neurosci., vol. 14, p. 593, 2020. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2020.00593
F. McLoughlin, A. Duffy, and M. Conlon, "Evaluation of time series techniques to characterise domestic electricity demand," Energy, vol. 50, pp. 120-130, 2013. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2012.11.048
E. Cano, R. Salcedo, and G. Soto, "Analisis de principios y aplicaciones de la transformada wavelet," Universidad Nacional de Catamarca, 2010.
J. Olbrys and M. Mursztyn, "Measuring stock market resiliency with discrete fourier transform for high frequency data," Physica A, vol. 513, pp. 248-256, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physa.2018.09.028
M. Sanabria-Villamizar, M. Bueno-Lopez, J. C. Hernandez, and D. Vera, "Characterization of household-consumption load profiles in the time and frequency domain," Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst., vol. 137, p. 107756, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijepes.2021.107756
R. Sharma, R. B. Pachori, and S. Gautam, "Empirical mode decomposition based classification of focal and non-focal eeg signals," in Proc. 2014 Int. Conf. Med. Biometrics, 2014, pp. 135-140. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICMB.2014.31
M. A. Colominas, G. Schlotthauer, P. Flandrin, and M. E. Torres, "Descomposicion empirica en modos por conjuntos completa con ruido adaptativo y aplicaciones biomedicas," in Proc. XVIII Cong Arg. Bioing. y VII Jorn. Ing. Clinica, Mar del Plata, Argentina, 2011.
Y. Lei, J. Lin, Z. He, and M. J. Zuo, "A review on empirical mode decomposition in fault diagnosis of rotating machinery," Mech. Syst. Signal Process, vol. 35, no. 1-2, pp. 108-126, 2013. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2012.09.015
O. B. Fosso and M. Molinas, "Emd mode mixing separation of signals with close spectral proximity in smart grids," in Proc. 2018 IEEE PES innovat. smart grid technolog. conf. (ISGT-Europe), 2018, pp. 1-6. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISGTEurope.2018.8571816
M. Bueno-Lopez, M. Molinas, and G. Kulia, "Understanding instantaneous frequency detection: A discussion of hilbert-huang transform versus wavelet transform," in Proc. Int. Work-Conf. Time Ser. Anal.-ITISE, vol. 1, 2017, pp. 474-486.
G. L. Goldberger AL, Amaral LAN, "Physiobank, physiotoolkit, and physionet: Components of a new research resource for complex physiologic signals, 2000. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.101.23.e215
C. Gomez, P. Arbelaez, M. Navarrete, C. Alvarado-Rojas, M. Le Van Quyen, and M. Valderrama, "Automatic seizure detection based on imaged-eeg signals through fully convolutional networks," Sci. Rep., vol. 10, no. 1, pp. 1-13, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-78784-3
J. Malmivuo and R. Plonsey, "Bioelectromagn. EEG," Jan. 1995, pp. 247-264.
A. H. Shoeb and J. V. Guttag, "Application of machine learning to epileptic seizure detection," in Proc. ICML, 2010.
M. A. Rodriguez, J. F. Sotomonte, J. Cifuentes, and M. Bueno-Lopez, "A classification method for power-quality disturbances using hilbert-huang transform and lstm recurrent neural networks," J. Electr. Eng. Technol., vol. 16, pp. 249-266, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42835-020-00612-5
M. Uyar, S. Yildirim, and M. T. Gencoglu, "An expert system based on s-transform and neural network for automatic classification of power quality disturbances," Expert Syst. Appl., vol. 36, no. 3, pp. 5962-5975, 2009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2008.07.030
F. Series, "Fourier series & fourier transforms," BioMed. Eng., 2003.
M. Zabihi, S. Kiranyaz, A. B. Rad, A. K. Katsaggelos, M. Gabbouj, and T. Ince, "Analysis of high-dimensional phase space via poincare section for patient-specific seizure detection," IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng., vol. 24, no. 3, pp. 386-398, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNSRE.2015.2505238
N. E. Huang, Hilbert-Huang transform and its appl. World Scientific, 2014, vol. 16. https://doi.org/10.1142/8804
N. E. Huang et al., "The empirical mode decomposition and the hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis," Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A math. Phys. Eng Sci, vol. 454, no. 1971, pp. 903-995, 1998. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspa.1998.0193
P. N. Jadhav, D. Shanamugan, A. Chourasia, A. R. Ghole, A. Acharyya, and G. Naik, "Automated detection and correction of eye blink and muscular artefacts in eeg signal for analysis of autism spectrum disorder," in Proc. 2014 36th Annu. Int. Conf. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc., 2014, pp. 1881-1884. https://doi.org/10.1109/EMBC.2014.6943977
M. Peel, G. Pegram, and T. McMahon, "Empirical mode decomposition: improvement and application," in Proc. Int. Congress Model. Simul., vol. 1. Citeseer, 2007, pp. 2996-3002.
M. Bueno-Lopez, M. Sanabria-Villamizar, M. Molinas, and E. Bernal-Alzate, "Oscillation analysis of low-voltage distribution systems with high penetration of photovoltaic generation," Electr. Eng., vol. 103, no. 2, pp. 1141-1154, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-020-01152-x
C. Rehtanz, Y. Li, Y. Cao, and D. Yang, "Interconnected power systems: Wide-area dynamic monitoring and control applications," 2016.
Z. Wu and N. E. Huang, "Ensemble empirical mode decomposition: a noise-assisted data analysis method," Adv. Adapt. Data Anal., vol. 1, no. 01, pp. 1-41, 2009. https://doi.org/10.1142/S1793536909000047
A. R. Messina, V. Vittal, G. T. Heydt, and T. J. Browne, "Nonstationary approaches to trend identification and denoising of measured power system oscillations," IEEE Trans. Power Syst., vol. 24, no. 4, pp. 1798-1807, 2009. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPWRS.2009.2030419
How to Cite
APA
ACM
ACS
ABNT
Chicago
Harvard
IEEE
MLA
Turabian
Vancouver
Download Citation
Recibido: 27 de septiembre de 2023; Aceptado: 9 de abril de 2024
Abstract
Context:
Epilepsy is a neurological disease that affects more than 50 million people worldwide, causing recurrent seizures, with a significant impact on patients’ quality of life due to abnormally synchronized neuronal activity.
Method:
This article discusses three methods used for signal analysis in patients diagnosed with epilepsy. Conventional signal decomposition methods, such as the fast Fourier transform, widely used in signal analysis based on time series techniques, have some issues when analyzing nonlinear and non-stationary signals, in addition to difficulties in detecting low-order frequencies.
Results:
To overcome these limitations, alternatives such as empirical mode decomposition and one of its variants, called ensemble empirical mode decomposition, have been developed.
Conclusions:
In this study, the results obtained through the aforementioned techniques were compared, revealing the impact of nonlinear methods on the reconstruction of brain activity. electroencephalogram, empirical mode decomposition, epilepsy, instantaneous frequency, intrinsic mode functions, methodology, nonlinear, non-stationary, oscillation modes, seizures.
Keywords:
These techniques allow observing different oscillation modes through intrinsic mode functions and instantaneous frequencies..Resumen
Contexto:
La epilepsia es una enfermedad neurológica que afecta a más de 50 millones de personas en todo el mundo, provocando convulsiones recurrentes, con un impacto significativo en la calidad de vida de los pacientes debido a actividad neuronal anormalmente sincronizada.
Métodos:
Este artículo analiza tres métodos empleados para el análisis de señales en pacientes diagnosticados con epilepsia. Los métodos de descomposición de señales convencionales, como la transformada rápida de Fourier, ampliamente utilizada en el análisis de señales basado en técnicas de series de tiempo, presentan algunos problemas al analizar señales no lineales y no estacionarias, así como dificultades para detectar frecuencias de bajo orden.
Resultados:
Para superar estas limitaciones, se han desarrollado alternativas como la descomposición empírica de modos y una de sus variantes, llamada descomposición modal empírica de conjunto. Estas técnicas permiten observar diferentes modos de oscilación mediante las funciones de modo intrínseco y las frecuencias instantáneas.
Conclusiones:
En este estudio se compararon los resultados obtenidos mediante las técnicas mencionadas, revelando el impacto de los métodos no lineales en la reconstrucción de la actividad cerebral.
Palabras clave:
electro encefalograma, descomposición epmírica de modos, epilepsia, frecuencia instantánea, funciones de modo intrínseco, metodología, no lineal, no estacionario, modos de oscilación, convulsiones.Introduction
Throughout the 20th century, important advancesweremade in the study of epilepsy, thanks to the use of increasingly sophisticated techniques and tools 1. Among these techniques, electroencephalographic (EEG)monitoring is one of the most widely used for the diagnosis and detection of epileptic seizures2.EEG monitoring involves recording the electrical activity of the brain via electrodes placed on the scalp, and it can provide valuable information about epilepsy-related brain activity 3. However, the processing and analysis of EEG data must consider the difficulties associated with large volumes of information 4. Even today, medical professionals identify epileptic seizures by visual inspection, aided by the continuous monitoring of EEG signals, which is time-consuming and subject to human error 5. In this context, several signal analysis techniques have been developed to identify epilepsy-related patterns in EEG records, where the reconstruction of brain activity from the resulting frequency bands is performed 6. Neuroscience has established five frequency bands associated with epilepsy: the delta band (0-4 Hz), the theta band (4-8 Hz), the alpha band (8-14 Hz), the beta band (14-30 Hz), and the gamma band (30-150 Hz) 7.
The identification of epileptic seizures still represents an unsolved challenge in the field of neuroscience, which is why different techniques are still being developed to support the recognition and treatment of this pathology (8, 9). However, due to the complexity and variability of seizures, different methods and tools are required for identification and classification tasks. Therefore, different methodologies have been developed which are based on the use of brain signal recording techniques, such as electroencephalography (EEG), magnetoencephalography (MEG), and functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), as well as signal processing algorithms and machine learning techniques 10-12. These tools have proven to be effective in the identification and classification of seizures, allowing for a better diagnosis and treatment of epilepsy. These tools, derived from signal extraction methods, are mainly the Fourier transform (FT), the wavelet transform (WT), and the Hilbert Huang transform (HHT), as well as their variants 13. Depending on the signals to be analyzed, each of these methods has strengths and weaknesses 14.
The FT and its variants are ideal processing techniques for identifying signals in the time domain, aiming to transform a complicated problem into a solvable one. The FT is a basic tool in the analysis of non-periodic signals that have finite energy 15. However, it exhibits some issues when characterizing signals in short periods of time, as it is difficult to interpret the results 16.
The HHT has gained popularity in the analysis of nonlinear and non-stationary signals. It was initially used to study ocean waves, and its application has now been extended to various fields 17. A fundamental part of this method is empirical mode decomposition (EMD), a technique used for pattern identification in non-stationary and nonlinear signals 18. EMD can decompose signals into basic components known as intrinsic modes, which facilitates the identification of key patterns in signal analysis and frequency identification 19,20.
EMD, based on the HHT, also reports some issues related to the mode mixing problem, which is associated with the mechanism for extracting mono-components from a multi-component signal. As a result, only modes that clearly contribute their maxima and minima can be identified via EMD.
When a mode cannot clearly contribute with extremes, EMD will not be able to separate it into an intrinsic mode function (IMF), and it will remain mixed with another IMF, turning it into noise and causing an inadequate interpretation of the results 21. To solve this problem, a variant known as ensemble empirical mode decomposition (EEMD) is employed, where a signal called adaptive noise is added to each of the IMFs obtained via EMD 22.
In recent decades, considerable progress has been made in the study of epilepsy, including the advancement of sophisticated techniques for seizure detection. In particular, nonlinear and non-stationary signal analysis methods have shown effectiveness in automatic seizure detection, and they are often used to solve problems that cannot be solved via traditional approaches.
This papercomparesthreedifferentmethodologiesforsignaldecomposition: FFT,EMD,andEEMD. The database is sorted, aiming for an organized dataset that aids in finding the most appropriate method, as well as the frequencies of interest for the detection of epileptic seizures. This document is structured as follows: Section 2 presents the signal decomposition methods and a description of the database used. Section 3 shows the results obtained with the proposed methodology, and Section 4 analyzes them. Finally, the conclusions derived from the study are stated in Section 5.
Methods
Dataset
The dataset used in the signal classification study was acquired from a freely available medical research data repository called Physionet, which contains signals collected from the scalp of intractable seizure patients at Boston Children’s Hospital. This information has been published on the Physionet website 23.
EEG signals were captured by placing electrodes on the scalp of patients using various configurations 24. The patients included both males and females in the ranges of 3-22 and 1.5-19 years old, respectively. The sampling frequency used was 256 samples per second, with a resolution of 16 bits. The nomenclature of the International 10-20 System was used to define the position of the electrodes on the scalp, with 23 channels available for each analyzed patient.
Fig. 1 shows the location of the electro desaccording to the International 10-20 System Configuration.
Figure 1: Location of electrodes according to the International 10-20 System 25
Experts in the field noted the onset and end of epileptic seizures for each of the recordings 26. In total, 941.6 h of interictal activity and 3 h of ictal activity were analyzed, which corresponded to the 181 seizures described in the database. From this database, we selected the signals with epileptic seizures to perform signal decomposition, obtaining 80 samples.
Signal decomposition methods
For many years, Fourier series analysis was ideal for studying signals in different fields, and it was assumed that conventional methods were sufficient to solve a particular problem 27. With the rise of new technologies, some issues emerged: the composition of signals was affected as more complex signals were being processed, which were assumed to be non-linear and non-stationary. These issues could be solved via traditional methods.
Thus, new signal decomposition methods were developed, such as the fast and the short-term Fourier transforms (FFT and STFT), which performed better but had some limitations 28. Subsequently, HHT emerged as a solution to problems that could not be solved with the previous methods, and researchers were refining and perfecting new strategies that generated better solutions. In this context, EMD and EEMD, nonlinear decomposition methods each with a better response than the previous one, were created. A brief description of FFT, EMD, and EEMD is provided below.
The fast Fourier transform (FFT)
The FT is one of the most widely used tools in engineering applications where the behavior of dynamic systems and periodic signals is studied in the time domain while considering their frequency content 29.
The FFT is an algorithm that allows understanding the behavior of a dataset in the frequency domain, based on the calculation of the discrete FT. Nevertheless, it has disadvantages in spectral analysis, such as aliasing and leakage, as well as with regard to the computation times needed to process data. In addition, it is difficult to detect low frequencies due to its inefficient resolution 17.
Signal processing and learning methods such as machine learning are valuable tools in EEG signal analysis, as they have been developed to diagnose seizures and epileptic attacks. The research conducted by 30 allowed extracting a set of features from the original signals of two datasets to be analyzed using FT and EMD, with the purpose of classifying and evaluating EEG signals. These authors proposed a methodology to compare the behavior of signal analysis methods using classifiers in order to obtain specific features in the time domain.
The Hilbert-Huang transform (HHT)
The development of HHT arose from the need to describe distorted nonlinear waves combined with variations of the signals that naturally occur in non-stationary processes 31. HHT integrates EMD and HT (developed by Huang). In this case, the EMD method decomposes signals into single components called IMFs, from which it is possible to obtain the amplitude a(t) and instantaneous frequencies. This method is widely employed for extracting information from a set of nonlinear and non-stationary data (fi(t)) 32. After this procedure, HT is used to obtain the corresponding Hilbert spectrum (HS).
The HS is a 3D representation of the instantaneous amplitude and the instantaneous frequency for each IMF as a function of time. The HS is defined as follows 22:

For a general multi-component signal, the HS is defined as the sum of the Hilbert spectra of all the IMFs, as indicated in

where Nis the total number of IMFs.
Empirical mode decomposition EMD
EMD is a tool for the analysis of nonlinear and non-stationary signals, which was proposed by Huang 33 and aims to decompose a nonlinear and non-stationary signal into a sum of IMFs while satisfying the following criteria 19,20:
1. In the entire data set, the number of extremes and the number of zero crossings must be equal or differ by 1 at most.
2. At any point, the mean value of the envelopes defined by the local maxima and the local minima is zero.
The second condition implies that an IMF is stationary, which simplifies its analysis. However, an IMF can exhibit changing amplitude and frequency modulation 34.
EMD has some issues, such as the presence of oscillations of unequal amplitude in one or more modes and similar oscillations in different modes, a phenomenon known as mode mixing. The screening process can be summarized in the following algorithm: decompose a dataset x(t) into IMFs xn(t) and a residual r(t), such that the signal can be represented as:

EMD has been adjusted to reduce the mode mixing phenomenon and thus ensure a better identification of the different frequencies in a process or system 35.
The EMDalgorithm for a signal can be summarized as follows 32,36:
1. Identify all extremes in x(t).
2. Calculate an upper envelope eu(t) and a lower envelope el(t) via interpolation.
3. Determine the local averages as m(t) = (eu(t) + em(l))/2.
4. Obtain the residual r(t) = x(t) + m(t).
5. Iterate until the number of zeros equals the number of zero crossings.
6. Subtract the obtained IMF from the original signal.
7. Iterate over the residual until the function becomes monotonic.
The authors of 30), who used FFT and EMD for signal decomposition, state that it is useful to employ EMD and subsequently extract the IMFs defined by the components of amplitude modulation (AM) and frequency modulation (FM). Nonlinear and non-stationary complex signals can be decomposed into a finite number of IMFs in the spectrum of the Hilbert transform. The authors present the different decomposition modes of EMD. Different classifiers are trained and evaluated to f ind the best methodology.
Ensemble empirical mode decomposition (EEMD)
EEMD arose as an alternative to eliminate mode mixing, the main issue of the EMD. This approach consists of adding noise to the signal, known as white Gaussian noise of finite amplitude, where the real IMF is found as the average of several IMFs 37. Assuming that the added noise is different for each of the IMFs, averaging them over a certain number of attempts should cancel the noise, obtaining a single part and the true IMF.
The proposed algorithm for EEMD is:
1. Add white noise to the signal.
2. Decompose the data added with white noise, using the EMD to obtain the IMFs.
3. Repeat steps 1 and 2 with different white noise in each iteration.
4. Obtain the average of the corresponding IMFs from the decomposition as the final result.
Astudy conducted by 6 analyzed EEG recordings using EMD and EEMD with several classifiers to identify the IMFs that best represented an original signal. After the IMF selection process, a set of features was created using IMF1, IMF2, and IMF3. According to the authors, the objective was to propose a hybrid method for IMF selection and explore the effect of these IMFs. Their work evaluated the advantages of using EEMD, decomposing versions of signals with added noise to address EMD’s modemixing issues. This approach yielded better results.
Instantaneous frequency (IF)
The concept of instantaneous frequency has become popular due to its effect on systems related to signal analysis, especially in nonlinear systems, where physical parameters derived from the signals are often characterized. Regardless of their behavior, most signals used to be analyzed via FT, which generates time-invariant frequency and amplitude values 35,38. As per the analysis proposed by Fourier, the frequency of a signal is derived from its period. However, the frequency of a non-stationary wave is hard to define. It is also possible to define the frequency as the angular velocity associated with the phase change rate. If it is possible to define a phase for a signal, it is possible to calculate its frequency (i.e., IF) 17.
Results and discusión
To evaluate the performance of the aforementioned decomposition methods, three signals from patients suffering from epileptic seizures were taken. By analyzing the behavior of the original signal, maximum values could be identified at different points, as shown in Fig. 2, which shows the three original signals corresponding to said patients.
Figure 2: Original signals
In signal 1, the maximum value was observed at time instant t = 1400 s. In signals 2 and 3, the maximumvalue was detected at t = 1800 and 700 s, respectively.
Signal decomposition using FFT
The FFT method was first implemented in MATLAB.Fig. 3 shows the results obtained after performing signal decomposition on three seizure signals in only one channel. The objective of this article is to show the frequency detected by each of the methods. Thus, three channels were selected, which allow for multiple frequencies.
Figure 3: Signal analysis using FFT
Signals 1 and 3 have several similarities; three maxima stand out at the same time instants i.e., t = 200, 1500, and 3000 s. This can be used to determine the points where seizures may be detected. After the instant t = 1500 s, the spectra does not grow as abruptly as before. Signal 2 does not exhibit notable maxima.
Signal decomposition using EMD
With the EMD method, the IMFs of each signal are obtained. EMD works as a natural filter of the original signals by separating them into frequency components, making it possible to observe the signals of interest. Fig. 4 shows the results obtained by applying EMD to the three signals.
In Fig. 4, IMFs 5 and 6 of signals 1, 2, and 3 clearly show the frequencies of interest for seizure detection. IMF 5 has maximum values of 15-17 Hz, and IMF 6 has maximum values of 8-9 Hz, representing the alpha and beta bands, respectively, i.e., where seizures may occur and where seizures may be initiated. Meanwhile, IMFs 1 and 2 show noise activity, and IMF 4 shows a better separation between modes.
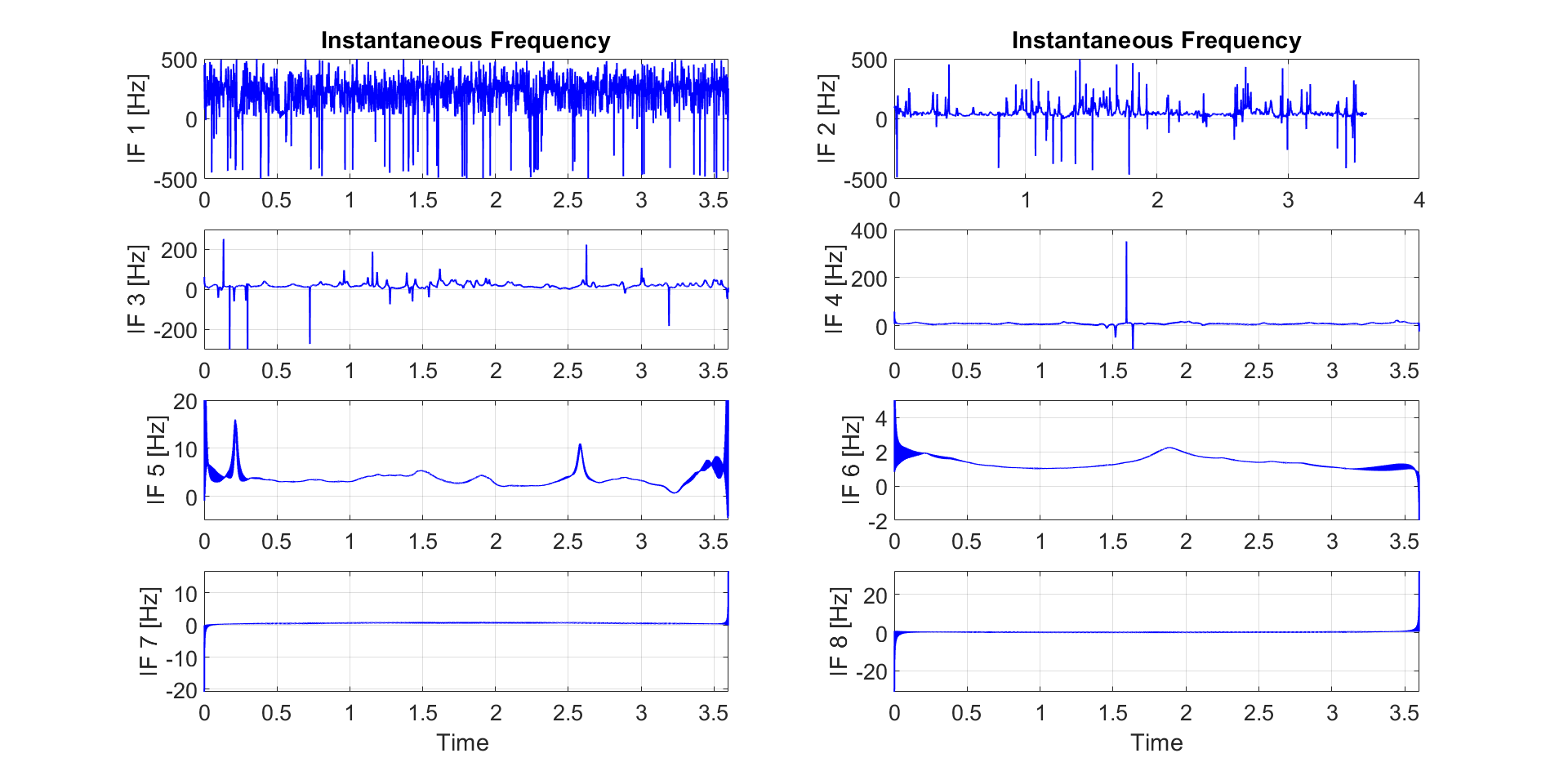
Subsequently, the results corresponding to the IFs of the analyzed signals are obtained. Fig. 5 shows these results.
Figure 4: Signal analysis using EMD
According to Fig. 5, the IF 5 of signals 1, 2, and 3 shows a maximum frequency value that oscillates between 10 and 15 Hz. This is in the alpha band and can be interpreted as an instance where a convulsion occurs.
Figure 5: Signal analysis with IF
Signal decomposition using EEMD
Fig. 6 shows the results obtained with EEMD, where noise is added to each of the signals to obtain a better separation of the IMFs and reduce mode mixing.
Figure 6: Signal analysis using EEM
In Fig. 6, IMFs 4 and 5 show the frequency bands where epileptic seizures may be detected, confirming the results obtained with EMD and IF in Figs. 4 and 5, respectively.
Based on the results obtained via the three signal decomposition methods, the following can be stated. Regarding the use of FFT, the results in Fig. 3 do not allow for a clear visualization of the signals of interest due to interference. Although it is possible to observe two maxima in signals 1 and 3, their meaningcannotbedetermined, whichmakesitdifficult to interpret the results and provide a conclusive answer. The analysis supports the position of 14, suggesting that each of these methodologies has both advantages and limitations. One of the disadvantages associated with decomposition is its low resolution in the time-frequency domain, which is evident in Fig. 3. In addition, the results of the FFT show alowresolution due to the non-linearity of the signal.
Furthermore, as emphasized in 15, the results demonstrate the challenges associated with interpreting signals using short time intervals due to their complex dynamics.
In this vein, FFT is not the best method to decompose non-linear and non-stationary signals where harmonic and non-harmonic components can appear. While FFT is still a valuable tool in many signal processing scenarios, its compatibility with signals exhibiting non-linearity and non-stationarity is notably sub-optimal. Thus, alternative methods that provide improved precision and adaptability to such signals should be explored.
On the other hand, when obtaining IMFs and IFs via EMD, the neuronal activity of each channel shows, in greater detail, the frequencies of interest for epileptic seizures occur. In this case, the alpha and beta frequency bands are those of greatest interest. The beta band is represented in IMF 6, and the alpha band in IMF 5. These frequency bands represent the main brain activity for our study, since they represent the onset and course of a seizure. According to the figures, the frequency increases and the amplitude decreases in IMF 5, whereas, in IMF 6, the frequency decreases and the amplitude increases.
Applying EMD has yielded notably improved results compared to the FFT method. Therefore, the authors of 30 chose to employ FFT and EMD to identify the most appropriate method for detecting epileptic seizures. Upon verifying the results, it became evident that employing EMD resulted in greater clarity and improved interpretation. These findings were further corroborated in 31, where the acquisition of IMFs validated the significance of conducting this procedure, as it enables the decomposition of a finite number of IMFs in the spectrum of the Hilbert transform, integrating both HT and EMD.
EMD’s adaptability to non-linear and non-stationary signals provides a more accurate representation of the underlying components, enhancing the precision and interpretability of the results.
Using EEMD confirms the results obtained with the IMFs and the IFs of signals 1, 2, and 3. In IMF 5, the alpha band is of greater interest than the others because it enables the clear visualization of neuronal activity over time. Utilizing EEMD in the analysis yields better results than EMD and FFT. EEMD’s ability to address non-linear and non-stationary signal characteristics, coupled with its noise robustness, significantly improved the quality and accuracy of our findings. In comparison with EMD, EEMD’s ensemble approach introduces enhanced stability and precision with regard to mode extraction, mitigating issues such as mode mixing.
Validating the results of 6, we found that, by employing EMD while obtaining the IMFs, the EEMD yields results of higher reliability than those provided by EMDalone. Thesefindingsreinforcethenotion that integrating EEMD into the analysis represents a significant advance in terms of the quality and accuracyoftheresults, whichhasimportantimplicationsforthepracticalapplicationofthesetechniques in the field of epileptic seizure detection and diagnosis.
Table I showsthemostsignificant frequency values obtained using each of the signal decomposition methods for epileptic seizure detection. FFT does not allow determining specific frequency values, hindering the interpretation of the results.
Table I: Frequency values obtained with the studied decomposition methods

Finally, Table II shows the strengths and weaknesses of the decomposition methods discussed above.
Table II: Strengths and weaknesses of signal decomposition methods

This study compared the efficacy of three signal processing techniques for epileptic seizure signal analysis. FFT excels in revealing frequency components but may miss nonlinear features. EMD captures nonlinear and non-stationary characteristics but is sensitive to noise, and EEMD, as an extension of EMD, offers improved noise robustness and adaptability to non-stationary signals. This comparative assessment aims to elucidate the strengths and limitations of these methods, aiding researchers in selecting the most suitable approach for their specific epilepsy research needs.
Conclusions
According to the state of the art and the research background, the brain can exhibit activity at frequencies between 0.5 Hz for Delta waves and 45 Hz for Gamma waves, and, by correctly detecting these frequencies, it is possible to diagnose different pathologies, with epilepsy being one of the most interesting. The use of time-frequency decomposition methods for EEG signals is generally applied in the study of brain processes associated with activity at certain frequencies, and it constitutes one of the main advantages of EMD and its variations (i.e., EEMD).
EMD has shown the ability to separate signals using time-frequency decomposition in various contexts. For example, this method is widely employed to analyze nonlinear and non-stationary signals in fields such as medicine, power systems, image processing, weather forecasting, and climate analysis, among others.
The Fourier transform is a widely used method in different applications. However, it has some issues when it comes to dealing with low-order frequencies, at which epilepsy is detected. With the results presented in this article, it should be possible to establish a way to adequately detect epileptic seizures by calculating instantaneous frequencies
References
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Leandro Dorado-Romero, Maximiliano Bueno-López, Jenny Alexandra Cifuentes

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
From the edition of the V23N3 of year 2018 forward, the Creative Commons License "Attribution-Non-Commercial - No Derivative Works " is changed to the following:
Attribution - Non-Commercial - Share the same: this license allows others to distribute, remix, retouch, and create from your work in a non-commercial way, as long as they give you credit and license their new creations under the same conditions.










2.jpg)