DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14483/23448393.19067Published:
2023-04-29Issue:
Vol. 28 No. 2 (2023): May-AugustSection:
Chemical, Food, and Environmental EngineeringEvaluación de protocolos de síntesis de nanopartículas de cobre u óxidos de cobre
Evaluation of Protocols for the Synthesis of Copper or Copper Oxides Nanoparticles
Keywords:
nanoparticles, copper, copper oxides, chemical synthesis, biological synthesis (en).Keywords:
nanopart´ıculas, cobre, s´ıntesis biol´ogica (es).Downloads
References
R. Singla, A. Guliani, A. Kumari y S. K. Yadav, “Metallic Nanoparticles, Toxicity Issues and Applications in Medicine,” en Nanoscale Materials in Targeted Drug Delivery, Theragnosis and Tissue Regeneration, 1.a ed., Springer, Singapore, 2016, pp. 41-71. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-0818-4_3 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-0818-4_3
R. A. Sperling y W. J. Parak, “Surface modification, functionalization and bioconjugation of colloidal inorganic nanoparticles,” Trans. R. Soc. A, vol. 368, pp. 1333-1383, 2010. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsta.2009.0273 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1098/rsta.2009.0273
H. Kumar K, N. Venkatesh, H. Bhowmik y A. Kuila, “Metallic nanoparticle: a review,” BJSTR, vol. 4, n.o 2, pp. 3765-3775, 2018. https://doi.org/10.26717/BJSTR.2018.04.0001011 DOI: https://doi.org/10.26717/BJSTR.2018.04.0001011
A. Y. Ghidan y T. M. A. Antary, “Applications of nanotechnology in agriculture,” en Applications of Nanobiotechnology, 2020, pp. 1-14. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.88390
R. H. Lira Saldívar, B. Méndez Argüello, G. D. los Santos Villarreal et al., “Potencial de la nanotecnología en la agricultura,” Acta univer., vol. 28, n.o 2, pp. 9-24, 2018. https://doi.org/10.15174/au.2018.1575 DOI: https://doi.org/10.15174/au.2018.1575
S. Baker, T. Volova, S. Prudnikova, Svetlana V. Satish y N. Prasad M.N., “Nanoagroparticles emerging trends and future prospect in modern agriculture system,” Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol., vol. 53, n.o 53, pp. 10-27, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2017.04.012 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2017.04.012
B. Khodashenas y H. R. Ghorbani, “Synthesis of copper nanoparticles: An overview of the various methods,” Korean J. Chem. Eng., vol. 31, n.o 7, pp. 1105-1109, jul. 2014. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-014-0127-y DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-014-0127-y
M. C. Crisan, M. Teodora y M. Lucian, “Copper Nanoparticles: Synthesis and Characterization, Physiology, Toxicity and Antimicrobial Applications,” Appl. Sci., vol. 12, n.o 1, 2021. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12010141 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/app12010141
H. J. Lee, J. Y. Song y B. S. Kim, “Biological synthesis of copper nanoparticles using Magnolia kobus leaf extract and their antibacterial activity,” J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol., vol. 88, n.o 11, pp. 1971-1977, nov. 2013. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.4052 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.4052
D. Ray, S. Pramanik, R. P. Mandal, S. Chaudhuri y S. De, “Sugar-mediated ‘green’ synthesis of copper nanoparticles with high antifungal activity,” Mater. Res. Express, vol. 2, n.o 10, pp. 105 002, oct. de 2015. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/2/10/105002 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/2/10/105002
S. Adewale, A. Similoluwa, F. Adekunle y A. Kolawole, “Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles for biomedical application and environmental remediation,” Heliyon, vol. 6, n.o 7, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04508 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04508
M. A. Asghar y M. A. Asghar, “Green synthesized and characterized copper nanoparticles using various new plants extracts aggravate microbial cell membrane damage after interaction with lipopolysaccharide,” International journal of biological macromolecules, vol. 160, pp. 1168-1176, oct. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.05.198 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.05.198
S. S. Shankar, A. Rai, A. Ahmad y M. Sastry, “Rapid synthesis of Au, Ag, and bimetallic Au core-Ag shell nanoparticles using Neem (Azadirachta indica) leaf broth,” J. Colloid. Interface Sci., vol. 275, n.o 2, pp. 496-502, jul. 2004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2004.03.003 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2004.03.003
S. Shankar y J. W. Rhim, “Effect of copper salts and reducing agents on characteristics and antimicrobial activity of copper nanoparticles,” Mater. Lett., vol. 132, pp. 307-311, oct. 2014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2014.06.014 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2014.06.014
S. Chandra, A. Kumar y P. K. Tomar, “Synthesis and characterization of copper nanoparticles by reducing agent,” J. Saudi Chem. Soc., vol. 18, n.o 2, pp. 149-153, abr. de 2014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jscs.2011.06.009 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jscs.2011.06.009
G. Madras y B. J. McCoy, “Temperature effects on the transition from nucleation and growth to Ostwald ripening,” Chem. Eng. Sci., vol. 59, n.o 13, pp. 2753-2765, jul. 2004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2004.03.022 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2004.03.022
Y. Qu, H. Yang, N. Yang, Y. Fan, H. Zhu y G. Zou, “The effect of reaction temperature on the particle size, structure and magnetic properties of coprecipitated CoFe2O4 nanoparticles,” Mater. Lett., vol. 60, n.o 29-30, pp. 3548-3552, dic. 2006. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2006.03.055 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2006.03.055
R. A. Soomro, S. T. Hussain Sherazi, Sirajuddin et al., “Synthesis of air stable copper nanoparticles and their use in catalysis,” Adv. Mater. Lett., vol. 5, n.o 4, pp. 191-198, abr. 2014. https://doi.org/10.5185/AMLETT.2013.8541 DOI: https://doi.org/10.5185/amlett.2013.8541
J. J. Lenders, G. Mirabello y N. A. Sommerdijk, “Bioinspired magnetite synthesis via solid precursor phases,” Chemical Science, vol. 7, n.o 9, pp. 5624-5634, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6SC00523C DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/C6SC00523C
T. Ameh y C. M. Sayes, “The potential exposure and hazards of copper nanoparticles: A review,” Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol., vol. 71, n.o junio, pp. 103-220, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2019.103220 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2019.103220
N. D. Pham, M. M. Duong, M. V. Le, H. A. Hoang y L. K. O. Pham, “Preparation and characterization of antifungal colloidal copper nanoparticles and their antifungal activity against Fusarium oxysporum and Phytophthora capsici,” C. R. Chim, vol. 22, n.o 11-12, pp. 786-793, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crci.2019.10.007 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crci.2019.10.007
U. Bogdanovi´c, V. Lazi´c, V. Vodnik, M. Budimir, Z. Markovi´c y S. Dimitrijevi´c, “Copper nanoparticles with high antimicrobial activity,” Mater. Lett., vol. 128, pp. 75-78, ago. 2014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2014.04.106 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2014.04.106
N. Pariona, A. I. Mtz-Enriquez, D. Sánchez-Rangle, G. Carrión, F. Paraguay-Delgado y G. Rosas-saito, “Green-synthesized copper nanoparticles as a potential antifungal against plant pathogens,” RSC, vol. 9, pp. 18 835-18 843, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9RA03110C DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/C9RA03110C
P. V. Viet, H. T. Nguyen, T. M. Cao y L. V. Hieu, “Fusarium Antifungal Activities of Copper Nanoparticles Synthesized by a Chemical Reduction Method,” J. of Nanomaterials, vol. 2016, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/1957612 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/1957612
A. Varympopi, A. Dimopoulou, I. Theologidis et al., “Bactericides based on copper nanoparticles restrain growth of important plant pathogens,” Pathogens, vol. 9, n.o 12, pp. 1-14, 2020. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9121024 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9121024
H. T. Luong, C. X. Nguyen, B. Thuong et al., “Antibacterial effect of copper nanoparticles produced in a Shewanella -supported non-external circuit bioelectrical system on bacterial plant pathogens,” RSC Adv., vol. 12, n.o 7, pp. 4428-4436, feb. de 2022. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1RA08187J DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/D1RA08187J
G. Dinda, D. Halder, C. Vázquez-Vázquez, M. A. Lopez-Quintela y A. Mitra, “Green Synthesis of Copper Nanoparticles and Their Use in Biomedical Applications,” J. Surf. Sci. Technol., vol. 31, n.o September, pp. 1-3, 2015.
J. Xiong, Y. Wang, Q. Xue y X. Wu, “Synthesis of highly stable dispersions of nanosized copper particles using L-ascorbic acid,” Green Chemistry, vol. 13, n.o 2011, pp. 900-904, 2011. https://doi.org/10.1039/C0GC00772B DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/c0gc00772b
S. Kothai y U. R, “Green Synthesis, Characterization of Copper Nanoparticles Derived from Ocimum Sanctum Leaf Extract and their Antimicrobial Activities,” J. chem. chem. sci., vol. 8, n.o 7, pp. 984-992, 2018. http://dx.doi.org/10.29055/jccs/670 DOI: https://doi.org/10.29055/jccs/670
S. Banerjee y D. Chakravorty, “Optical absorption by nanoparticles of Cu2O,” EPL, vol. 52, pp. 468-473, 4 2000. https://doi.org/10.1209/epl/i2000-00461-5 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1209/epl/i2000-00461-5
R. Cuevas, N. Durán, M. C. Diez, G. R. Tortella y O. Rubilar, “Extracellular biosynthesis of copper and copper oxide nanoparticles by Stereum hirsutum, a native white-rot fungus from chilean forests,” J. Nanomater., vol. 2015, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/789089 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/789089
M. Mallik, S. Monia, M. Gupta, A. Ghosh, M. P. Toppo y H. Roy, “Synthesis and characterization of Cu2O nanoparticles,” J. Alloys Compd., vol. 829, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.154623 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.154623
Y. Abboud, T. Saffaj, A. Chagraoui et al., “Biosynthesis, characterization and antimicrobial activity of copper oxide nanoparticles (CONPs) produced using brown alga extract (Bifurcaria bifurcata),” Appl. Nanosci., vol. 4, pp. 571-576, jun. de 2014. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-013-0233-x DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-013-0233-x
R. M. Silverstein, F. X. Webster y D. J. Kiemle, “Infrared Spectrometry,” en Spectrometric Identification of Organic Compounds, Seventh, NY, USA: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, 2005, pp. 72-18.
J. M. Jacob, M. S. John, A. Jacob et al., “Bactericidal coating of paper towels via sustainable biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Ocimum sanctum leaf extract,” Mater. Res. Express, vol. 6, n.o 4, pp. 45 401, 2019. https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/2053-1591/aafaed DOI: https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aafaed
E. A. Mohamed, “Green synthesis of copper & copper oxide nanoparticles using the extract of seedless dates,” Heliyon, vol. 6, n.o 1, e03123, ene 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e03123 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e03123
A. M. Raspolli Galletti, C. Antonetti, M. Marracci, F. Piccinelli y B. Tellini, “Novel microwavesynthesis of Cu nanoparticles in the absence of any stabilizing agent and their antibacterial and antistatic applications,” Appl. Surf. Sci., vol. 280, pp. 610-618, sep. 2013. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.05.035 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.05.035
F. Kurd, M. Fathi y H. Shekarchizadeh, “Basil seed mucilage as a new source for electrospinning: Production and physicochemical characterization,” Int. J. Biol. Macromol., vol. 95, pp. 689-695, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.11.116 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.11.116
M. Rafique, A. J. Shaikh, R. Rasheed et al., “Aquatic Biodegradation of Methylene Blue by Copper Oxide Nanoparticles Synthesized from Azadirachta indica Leaves Extract,” J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater., vol. 28, n.o 6, pp. 2455-2462, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-018-0921-9 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-018-0921-9
V. V. T. Padil y M. Cˇ ern´ık, “Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using gum karaya as a biotemplate and their antibacterial application,” Int. J. Nanomedicine, vol. 8, pp. 889-898, 2013. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S40599 DOI: https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S40599
M. Rai, A. P. Ingle, R. Pandit et al., “Copper and copper nanoparticles: Role in management of insect-pests and pathogenic microbes,” Nanotechnol. Rev., vol. 7, n.o 4, pp. 303-315, ago. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1515/ntrev-2018-0031 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1515/ntrev-2018-0031
How to Cite
APA
ACM
ACS
ABNT
Chicago
Harvard
IEEE
MLA
Turabian
Vancouver
Download Citation
Recibido: 2 de febrero de 2022; Revisión recibida: 23 de junio de 2022; Aceptado: 1 de noviembre de 2022
Resumen
Contexto:
Las nanopartículas de cobre u óxidos de cobre son materiales de interés para la agricultura por sus múltiples propiedades, entre ellas su actividad antimicrobiana, que resulta útil en el control biológico de plagas. Diversos autores han reportado que las nanopartículas con tamaño inferior a 50 nm tienen mayor efecto antimicrobiano. De acuerdo con esto, este estudio tuvo como objetivo comparar diferentes protocolos de síntesis de nanopartículas de cobre u óxidos de cobre, con el propósito de obtener NPs de tamaños adecuados para su futura evaluación en el control biológico de especies que afectan comúnmente los cultivos en Colombia.
Método:
Se evaluaron cinco protocolos de síntesis, cuatro de ellos clasificados como métodos de síntesis química verde y el otro como síntesis biológica. Las nanopartículas obtenidas fueron caracterizadas mediante espectroscopía UV-Vis, DLS, TEM, FTIR, DRX, SEM y EDS.
Resultados:
El protocolo 3, que utiliza sulfato de cobre pentahidratado como sal precursora, ácido ascórbico como agente reductor y almidón como estabilizante, resultó ser el más adecuado, pues con él se obtuvieron nanopartículas esféricas de cobre metálico con un tamaño promedio de 4,5 nm.
Conclusiones:
Fue posible comparar las metodologías de obtención de nanopartículas de cobre y óxidos de cobre, analizar el efecto de las condiciones de síntesis en sus características y finalmente obtener un protocolo para sintetizar nanopartículas de cobre con un tamaño adecuado para un potencial uso en aplicaciones de control biológico.
Palabras clave:
nanopartículas, cobre, óxidos de cobre, síntesis química, síntesis biológica..Abstract
Context:
Copper or copper oxide nanoparticles are materials of interest in the field of agriculture due to their multiple properties, including their antimicrobial activity, which is useful in the biological control of pests. Several authors have reported that nanoparticles smaller than 50 nm have a greater antimicrobial effect. Accordingly, this study aimed to compare different synthesis protocols, with the purpose of obtaining copper or copper oxide nanoparticles with adequate size for their subsequent evaluation in the biological control of species that commonly affect crops in Colombia.
Method:
Five synthesis protocols were evaluated, four of them classified as green chemical synthesis methods, and the other as biological synthesis. The obtained nanoparticles were characterized via UV-Vis spectroscopy, DLS, TEM, FTIR, XRD, SEM, and EDS.
Results:
Protocol 3, which uses copper sulfate pentahydrate as precursor salt, ascorbic acid as reducing agent, and starch as stabilizer, proved to be the most suitable, as spherical metallic copper nanoparticles with a size of 4,5 nm were obtained with it.
Conclusions:
It was possible to compare methodologies for copper and copper oxide nanoparticles production, analyze the effect of synthesis conditions on their characteristics, and finally obtain a protocol to synthesize copper nanoparticles with an adequate size for potential use in biological control applications.
Keywords:
nanoparticles, copper, copper oxides, chemical synthesis, biological synthesis..Introducción
Las nanopartículas (NPs) de naturaleza metálica y de óxidos de metales son ampliamente estudiadas en la ciencia y la ingeniería debido a sus propiedades ópticas, electrónicas, químicas, físicas y mecánicas. Estas propiedades están ligadas al tamaño, la estructura cristalina, la morfología y la composición de las partículas 1. Entre las características que poseen las NPs se encuentra su alta relación área superficial/volumen, lo cual favorece el incremento de la energía interfacial, la reactividad de la nanopartícula, la eficiencia en la absorción y la capacidad de ser funcionalizadas con moléculas de interés 2, 3.
En la agricultura, la nanotecnología se ha enfocado en el desarrollo de herramientas que ayuden a fortalecer el sector agrícola desde distintas aplicaciones, como el desarrollo de nanoformulaciones de agroquímicos para aplicar pesticidas y fertilizantes para el mejoramiento de los cultivos; el uso de nanosensores en la protección de cultivos para la identificación de enfermedades y residuos de agroquímicos; el empleo de nanodispositivos para la ingeniería genética de las plantas; los diagnósticos de enfermedades en plantas; y el manejo poscosecha 4. Actualmente, este sector se enfrenta a múltiples desafíos como el control de plagas, la absorción de nutrientes en los suelos, el mejoramiento genético de plantas, la detección temprana de patógenos, el manejo de recursos naturales, contaminantes en productos alimenticios, entre otros. Aunque el manejo de todas estas problemáticas se ha hecho empleando distintas herramientas, algunas son muy costosas y otras siguen siendo inútiles o poco efectivas 5.
Una de las posibles soluciones es el uso de NPs metálicas que, entre otras propiedades interesantes, tienen propiedades antimicrobianas. Las nanopartículas de cobre (CuNPs) u óxidos de cobre (CuONPs) poseen dichas propiedades y, además, son de bajo costo y fácil obtención. Estas nanopartículas han sido utilizadas para múltiples aplicaciones como fungicidas y bactericidas, así como para promover el crecimiento de las plantas 6. Las propiedades de las NPs están ligadas a su tamaño y forma 7, y, a su vez, estas características dependen del método de síntesis utilizado, que puede ser físico, químico o biológico.
En los métodos físicos, las NPs se generan mediante la reducción del tamaño del material original; las NPs obtenidas no presentan contaminación por solventes y tienen una distribución uniforme, lo cual constituye una mejora con respecto a la síntesis química. Sin embargo, en los métodos físicos se requieren equipos costosos y un alto uso de energía 8.
En la síntesis química se utilizan reactivos para la reducción de los iones cobre, y el mayor inconveniente que se presenta es el uso de materiales tóxicos 9. Esto ha llevado a evaluar compuestos como el azúcar, el ácido ascórbico, el almidón, etc., los cuales resultan ambientalmente más amigables. A los procesos de síntesis que incluyen este tipo de compuestos se les llama química verde 10
Por su parte, los métodos biológicos utilizan bacterias, hongos y extractos de plantas como agentes reductores de los iones cobre 11. Estos métodos tienen la ventaja de que utilizan materiales más ecológicos, siendo más económicos, simples y sostenibles que los métodos químicos. Es preferible utilizar extractos de plantas para obtener NPs en lugar de usar microorganismos, pues es más difícil preservar los cultivos celulares 12. Estos extractos, además, son adecuados para la síntesis de NPs a gran escala 13.
Se ha observado que los cambios en la temperatura, el pH, la naturaleza del agente reductor y su concentración, entre otros factores, afectan el tamaño y la forma de las NPs obtenidas 14, 19.
Algunos estudios han demostrado que el tamaño de partícula influye directamente en la citotoxicidad. Las partículas más pequeñas tienen una mayor relación área superficial/volumen, lo cual aumenta la reactividad y facilita el transporte intracelular 20. Los autores de 21 evaluaron el efecto del tamaño (53, 84, 120 y 174 nm) y de la concentración de las CuNPs (5, 10 y 20 ppm) en la actividad anitifúngica contra los hongos patógenos Fusarium oxysporum y Phytophthora capsici, encontrando que el mayor grado de inhibición del crecimiento se logra al utilizar las NPs más pequeñas, correspondientes a un tamaño de 53 nm, a una concentración de 20 ppm.
22 estudiaron el efecto antimicrobiano de CuNPs de 5 nm en cepas de Escherichia coli (bacteria Gram-negativa), encontrando que, después de 2 horas de tratamiento con las NPs a una concentración de 32 ppm, se logró inhibir el crecimiento en un 100 %. Por último, a partir de ensayos con microscopio de fuerza atómica, los autores pudieron concluir que la cepa E. coli es susceptible a las CuNPs, pues se evidenciaron daños en la membrana celular. Por su parte, 23 propusieron la síntesis verde de fungicidas, que consistían en CuNPs preparadas en medio acuoso. Mediante experimentos in vitro, evaluaron la actividad antifúngica de dichas NPs contra los hongos patógenos de plantas Fusarium solani, Neofusicoccum sp. y Fusarium oxysporum, encontrando que, aunque la actividad antifúngica difiere para cada especie, las CuNPs inducen fuertes cambios morfológicos en el micelio, además de daño en las membranas celulares.
24 sintetizaron CuNPs y CuONPs a través del método de reducción química. La actividad antifúngica de las NPs obtenidas, con un tamaño promedio en el rango de 20 a 50 nm, se evaluó mediante ensayos contra Fusarium sp., encontrando que el diámetro de la colonia fúngica casi no aumenta y que el crecimiento se inhibe en un 93,98 % al emplear una concentración de NPs de 450 ppm después de incubación por 9 días.
Dada la comprobada actividad antimicrobiana que han demostrado las CuNPs y las CuONPs, resulta de gran interés evaluar metodologías de síntesis que permitan su obtención, y poder así posteriormente evaluar su potencial aplicación en el control biológico de plagas como Fusarium oxysporum, Ralstonia solanacearum spp. y Xanthomonas spp., las cuales afectan cultivos importantes para Colombia, como es el caso del plátano, el tomate, el pimentón, la berenjena y la papa 25) ,(26. De acuerdo con ello, el objetivo del presente estudio fue comparar diferentes protocolos para la síntesis de CuNPs y CuONPs a partir de métodos de química verde y biológica reportados en la literatura. La caracterización de las NPs sintetizadas se realizó mediante las técnicas de UV-Vis, DLS, TEM, FTIR, DRX, SEM y EDS, y, según el tamaño obtenido, se infirió un posible uso en aplicaciones de control biológico.
Materiales y métodos
Síntesis de nanopartículas de cobre u óxidos de cobre
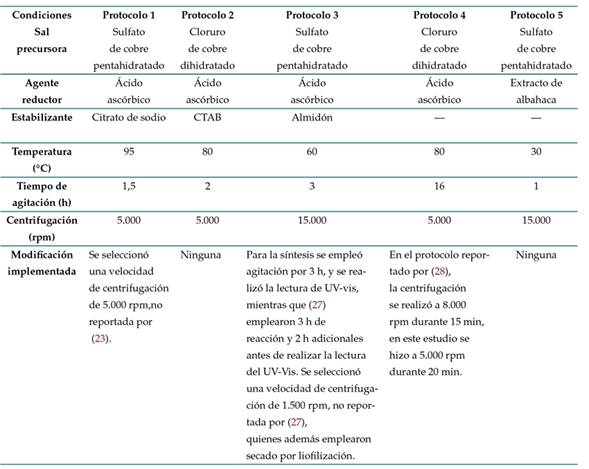
Con base en metodologías de síntesis de CuNPs reportadas en la literatura, se implementaron los protocolos que se describen a continuación. La Tabla I resume las principales condiciones evaluadas e indica si se realizó alguna modificación a la metodología. Los ensayos se realizaron por triplicado.
Métodos de química verde
-
Protocolo 1, basado en la metodología desarrollada por 23. Se preparó una solución de citrato de sodio tribásico dihidratado (PanReac AppliChem ITW Reagents) al 2.5 % m/V, se adicionaron 5 g de sulfato de cobre pentahidratado (Carlo Erba) y luego se agregaron, bajo agitación constante, 50 ml de ácido ascórbico (PanReac AppliChem ITW Reagents) 0,2 M y 30 ml de hidróxido de sodio (PanReac AppliChem ITW Reagents) 1 M. Finalmente, la mezcla se calentó a 95 °C durante 90 minutos y, cuando se formó un precipitado de color rojo, la solución se centrifugó, y el precipitado obtenido se almacenó en una nevera.
-
Protocolo 2, basado en la metodología desarrollada por 24. Se disolvieron 0,1712 g de cloruro de cobre dihidratado (Reactivos Ru) en 50 ml de agua desionizada. La solución se dejó en agitación hasta formar una solución homogénea de color azul. Después se adicionaron lentamente 10 ml de ácido ascórbico (PanReac AppliChem ITW Reagents) 0,1 M y, terminado este procedimiento, se ajustó el pH a 5 utilizando hidróxido de sodio (PanReac AppliChem ITW Reagents) 1 M. Posteriormente se agregaron lentamente 10 ml de CTAB (PanReac AppliChem ITW Reagents) 0,025 M, y la solución resultante se mantuvo a 80 °C hasta adquirir una coloración rojo-marrón. Al terminar el proceso, la solución se dejó enfriar a temperatura ambiente, y el precipitado obtenido conservó el color
-
Protocolo 3, basado en la metodología desarrollada por 27. Se disolvieron 2,5 g de almidón (Almidón Rey) en 15 ml de agua destilada, y se agitó a velocidad constante hasta obtener una mezcla homogénea. Luego, la solución de almidón se goteó a 10 ml de sulfato de cobre pentahidratado (Carlo Erba) 0,04 M, y se adicionó 1 g de ácido ascórbico (PanReac AppliChem ITW Reagents) directamente a la mezcla, la cual se mantuvo en agitación a velocidad constante durante 3 horas a 60 °C. La solución se centrifugó durante 5 minutos a 15.000 rpm, y el precipitado se refrigeró en nevera.
-
Protocolo 4, basado en la metodología propuesta por 28. Se calentaron 50 ml de una solución de cloruro de cobre dihidratado (Reactivos Ru) 0,01 M en baño María a 80 °C y se mantuvieron en agitación magnética. Posteriormente, se gotearon 50 ml de ácido ascórbico (PanReac AppliChem ITW Reagents) 0,4 M a la solución, manteniendo las mismas condiciones de calentamiento y agitación. La solución se mantuvo en agitación constante por un periodo de 16 horas hasta alcanzar la coloración esperada (café oscuro), y finalmente se centrifugó a 5.000 rpm durante 20 minutos
Método de síntesis biológica:
-
Protocolo 5, basado en la metodología desarrollada por 29. Se utilizó sulfato de cobre pentahidratado 0,5 M como sal precursora y extracto de hojas de albahaca morada (Ocimum sanctum) como agente reductor. Para obtener el extracto, se lavaron hojas frescas de albahaca morada, primero con agua corriente y después con agua destilada, para eliminar tierra e impurezas. Posteriormente se cortaron en pequeños pedazos y se tomaron 100 g, los cuales fueron agregados a 100 ml de agua destilada. Se realizó calentamiento a 60 °C durante 15 minutos, se filtró el extracto obtenido y se enfrió a temperatura ambiente. Para la síntesis de las NPs, se gotearon 50 ml de extracto de albahaca en una solución de 50 ml de sulfato de cobre 0,05 M. La mezcla se dejó reaccionar durante 24 horas a temperatura ambiente. Terminada la reacción, la solución se centrifugó a 15.000 rpm durante 10 minutos. Finalmente, se recuperó el precipitado y se almacenó en nevera.
Tabla I: Protocolos implementados
Caracterización de las nanopartículas de cobre
Para la caracterización se empleó espectroscopía UV-Vis con un equipo MAPADA 3200C, haciendo un barrido entre 200 y 800 nm para identificar el plasmón de resonancia superficial característico de las NPs de cobre u óxidos de cobre.
El tamaño y forma de las nanopartículas se midieron empleando las técnicas de microscopía eléctrónica de transmisión (TEM), utilizando el equipo Tecnai F20 Super Twin de FEI, y dispersión de luz dinámica (DLS), empleando un Zetasizer Lab con un índice de refracción de 1,54 correspondiente al cobre.
Las características morfológicas y la composición elemental se evaluaron empleando microscopía electrónica de barrido (SEM) y espectroscopía de rayos X por energía dispersiva (EDS), utilizando un microscopio electrónico JEOL-JSM 6490 LV, el cual opera con una aceleración de 20 V.
Mediante espectroscopía infrarroja se identificaron los grupos funcionales presentes en las muestras mediante un espectrofotómetro Alpha (Bruker®), tomando 32 escaneos con una resolución de 4 cm−1 y barriendo el espectro entre 500 hasta 4.000 cm−1 .
También se empleó la técnica de difracción de rayos X para determinar la cristalinidad y la composición de las fases. Esto, por medio del difractómetro Malvern-Panalytical, modelo Empryean 2012, con detector Pixel 3D y fuente de Cu (λ = 1,5418774) a 45 kV y 40 mA.
Se realizó análisis de caracterización en muestras específicas con base en las características y resultados obtenidos en las muestras analizadas.
Resultados
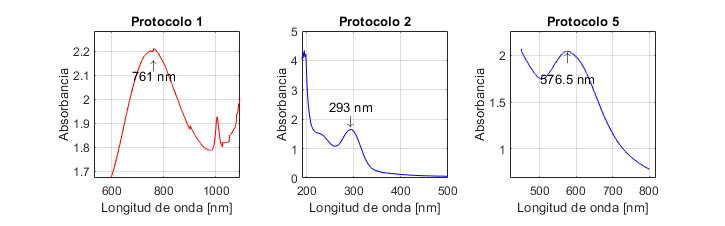
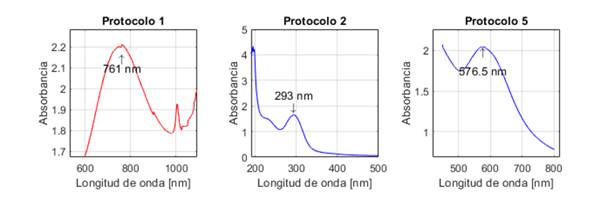
La Fig. 1 presenta los espectros UV-Vis de las NPs sintetizadas con los protocolos 1, 2 y 5. El espectro corresponde a un valor medio de absorbancia obtenido para cada protocolo con los tres ensayos realizados.
Figura 1: Espectros UV-Vis de las nanopartículas obtenidas con los protocolos de síntesis 1, 2 y 5
23 no realizaron caracterización mediante UV-Vis, por lo que no es posible saber si el máximo de absorción obtenido al emplear el protocolo 1 (761±0,3 nm) es acorde o no con sus resultados. Si bien la investigación de 30 reporta que las nanopartículas de óxido de cobre I (Cu2O) pueden presentar un máximo de absorción entre 590 y 800 nm, otros investigadores indican absorción a longitudes de onda entre 250 y 300 nm 31 y 560 y 650 nm 32. Por lo tanto, con el resultado de UV-Vis obtenido, no es posible inferir si hay formación o no de este tipo de NPs. Es por ello que dicho protocolo fue descartado.
Los resultados obtenidos con el protocolo 2 son diferentes a lo reportado por 24, quienes obtuvieron un pico de máxima absorción en 560 nm, atribuido a la formación de NPs de cobre. Por otro lado, en el presente estudio, dicho pico se obtuvo en 293±0,17 nm, lo cual, según (33), puede estar asociado a la presencia de NPs de óxido de cobre II (CuO). Por su parte, el trabajo de 31 reporta que el óxido de cobre I (Cu2O) puede ser monitoreado a través de los espectros UV-visibles, basándose en la formación de una banda del plasmón de resonancia superficial entre 250 y 300 nm. Es así que, a partir de estos datos, podría inferirse que en el presente estudio ocurrió oxidación de CuNPs, pues estas, cuando son expuestas a ambientes acuosos, son susceptibles a la oxidación, y el cobre se transforma en CuO y Cu2O
En cuanto al protocolo 5, 29 reportaron un pico de máxima absorción en 659 nm, el cual atribuyen a la presencia de CuNPs. Sin embargo, otros investigadores indican que los picos en una longitud de onda superior a 590 nm son característicos de NPs de óxido de cobre. Los estudios de 31 y 33 reportan picos de máxima absorción a 620 y 670 nm respectivamente. Ambos investigadores atribuyen dichos picos a la formación de nanopartículas de óxido de cobre II (CuO). En este estudio, la máxima absorción se obtuvo a 576±0,76 nm, longitud de onda cercana al intervalo de absorción (580-590 nm) reportado por 18 para las CuNPs
Cabe resaltar que la resonancia del plasmón de superficie es un fenómeno en el que los átomos interactúan entre ellos, generando una banda de resonancia característica al usar espectroscopía UV-Vis. Sin embargo, esta interacción se ve afectada por factores como el tamaño y forma de las NPs y la naturaleza y composición del medio de dispersión 31, por lo cual, dependiendo de la naturaleza de la NP, se obtiene un máximo de absorción en un intervalo u otro, y este, a su vez, puede presentar corrimientos. Esto podría explicar el desplazamiento de los picos de absorción y, por ende, la discrepancia con otros datos reportados en la literatura.
Por otro lado, no se observó un pico de absorción en la síntesis con los protocolos 3 y 4. A pesar de realizar las debidas diluciones de la muestra, no se logró una lectura adecuada. Los picos obtenidos representan únicamente el ruido del equipo y, por consiguiente, no se presenta el espectro. En el protocolo 3, basado en el reportado por 27, el espectro de UV-Vis obtenido presenta una banda de absorción muy tenue. Este estudio no obtuvo un resultado similar, posiblemente debido a que el tiempo de reacción empleado (3 horas) no fue suficiente para asegurar la reducción de todos los iones Cu2+ a cobre metálico, ya que la concentración de NPs en solución aumenta conforme ocurre la reacción de reducción, generando así una mayor absorbancia en el espectro UV-Vis. Cabe añadir que en 27 se empleó un total de 5 horas de reacción.
Para el caso del protocolo 4, los resultados difieren de los reportados por 28, debido posiblemente al efecto de la velocidad de centrifugación sobre la separación de NPs por tamaños -en este estudio se emplearon 5.000 rpm en vez de 8.000.
Es preciso añadir que se consideró realizar la caracterización de las muestras obtenidas con los protocolos 3, 4 y 5 mediante otras técnicas.
La Tabla II presenta los resultados obtenidos en el análisis de DLS. El ensayo se realizó por triplicado, y los valores corresponden al promedio. Con el protocolo 3 se obtuvieron valores inferiores a 1 µ, donde cerca del 27 % de las partículas tenían un tamaño de 27,8 nm y 14,6 % tenía un tamaño de 230 nm. Aunque no se obtuvo un espectro UV-Vis adecuado, sí se obtuvo la coloración rojo oscuro en la solución, tal y como lo reportan los autores del protocolo 27, quienes, además, obtuvieron un tamaño de partícula de 5,7±1,8 nm. El índice de polidispersidad es cercano a 1 tanto en el sobrenadante como en el precipitado, lo que indica que la distribución de tamaños es heterogénea y hay poblaciones de NPs grandes y pequeñas. Por otro lado, los tamaños de partícula obtenidos con el protocolo 4 son muy grandes; un 33 % de las partículas medía 1.039 nm. Estos resultados difieren mucho de los reportados por 28, quienes obtuvieron un tamaño de partícula de menos de 2 nm. Teniendo en cuenta lo anterior, así como el hecho de que no se obtuvo un espectro UV-Vis para la muestra sintetizada con el protocolo 4, este se descartó.
Tabla II: Resultados de DLS para sobrenadante y precipitado obtenidos con diferentes métodos de síntesis
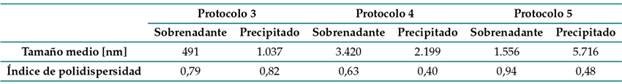
Con el protocolo 5, 29 obtuvieron un tamaño promedio de 29 nm; este estudio obtuvo 1.556 nm. Las diferencias en el tamaño promedio pueden deberse a que, al centrifugar a 15.000 rpm, las nanopartículas se aglomeraron, lo cual derivó en cúmulos de tamaño micrométrico. Sin embargo, en el análisis de DLS también se encontró que un 36,8 % de las partículas tenía un tamaño de 50,99 nm. El índice de polidispersidad del sobrenadante es casi 1, lo que significa que la muestra efectivamente tiene muchas partículas aglomeradas de diversos tamaños. Por el contrario, el índice de polidispersidad del precipitado es relativamente bajo e indica que el tamaño de partículas tiende a ser homogéneo.
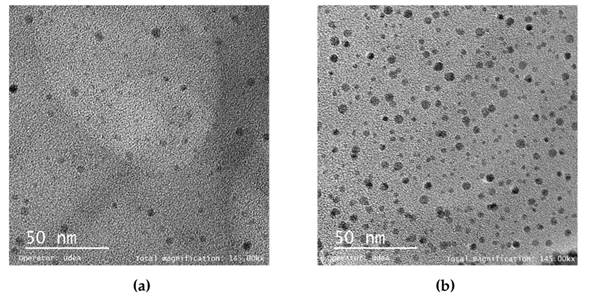
En la Fig. 2a, i.e., la imagen TEM para la muestra obtenida con el protocolo 3, se observa que las nanopartículas obtenidas tienen un tamaño de aproximadamente 4,5 nm y son de forma casi esférica. La Fig. 2b muestra las nanopartículas sintetizadas mediante el protocolo 5, con un tamaño de aproximadamente 5,03 nm y con la misma tendencia a ser esféricas.
Figura 2: Imágenes TEM de nanopartículas de cobre sintetizadas (a) con el protocolo 3 y (b) con el protocolo 5
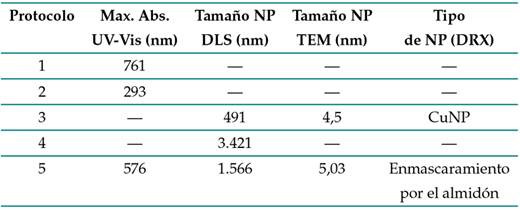
En la Tabla III se presenta un resumen de los resultados obtenidos con las diferentes técnicas de caracterización empleadas
Tabla III: Resultados de caracterización
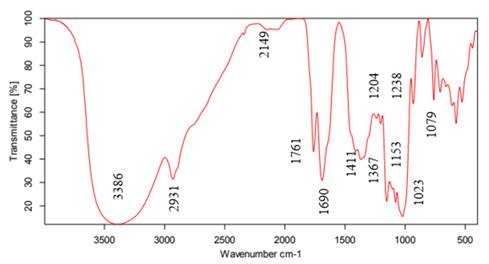
La Fig. 3 presenta el espectro FTIR obtenido para la muestra sintetizada empleando el protocolo 3. Según 34, las vibraciones por enlaces OH- son evidentes en la banda 3.386 cm−1 y pertenecen a los hidroxilos del almidón y el ácido ascórbico. Enseguida está la banda 2.931 cm−1 de los grupos CH2. Luego están 2.149 y 2.067 cm−1 por la vibración del grupo alquino (C≡C) y 1.761 cm−1 por la vibración de un grupo carbonilo (C=O), perteneciente a un éster. En la banda 1.690 cm−1 se encuentra C=C, que puede pertenecer al ácido ascórbico y puede estar desplazado porque el carbonilo y el oxígeno, al tener mayor densidad de carga, desplazan la banda a otras longitudes de onda. Después están las bandas 1.411 y 1.367 cm−1 , correspondientes a deformaciones fuera del plano de metilos y metilenos respectivamente. Las bandas 1.204 y 1.238 cm−1 son grupos C-O de ésteres. En 1.023 cm−1 se encuentra un grupo -COOH y, en 1.153 cm−1 , el movimiento vibracional de C-O de un éter. Las últimas bandas por debajo de 900 cm−1 pueden ser carbonos sustituidos con cobre y grupos CH sueltos.
Figura 3: Espectro FTIR de la solución obtenida con el protocolo 3
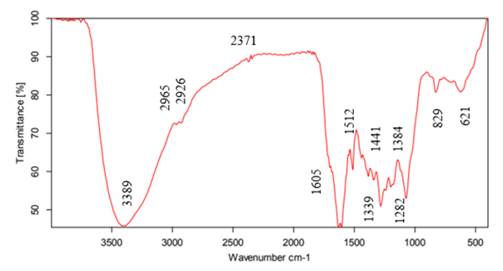
La Fig. 4 presenta el espectro infrarrojo para la muestra sintetizada con el protocolo 5. De acuerdo con 34, la primera banda, ubicada en 3.389 cm−1 , corresponde al estiramiento de enlaces -OH de alcoholes y fenoles. Enseguida se encuentran las bandas 2.965 y 2.926 cm−1 , correspondientes a deformaciones simétricas de metilos (CH3) y metilenos (CH2) respectivamente. En 2.371 cm−1 hay dos pequeños picos que evidencian la presencia de armónicos provenientes de grupos aromáticos, en 1.605 cm−1 hay una banda fuerte de un grupo carbonilo perteneciente a una cetona y en 1.512 cm−1 hay una banda desplazada de un grupo (C=C) debido a la presencia de grupos electroatrayentes. Las bandas 1.441 y 1.384 cm−1 corresponden a deformaciones por fuera del plano de grupos metilo (CH3) y metileno (CH2). En 1.339 cm−1 hay una mezcla de grupos -COOH y -OH de un éster. Las últimas dos bandas, 829 y 621 cm−1 , muestran la presencia de grupos aromáticos. Estos grupos funcionales coinciden con la presencia de compuestos en el extracto de albahaca, tales como el eugenol, el ácido ascórbico, los polifenoles, los flavonoides y las saponinas, entre otros 35. El grupo sulfonato aparece en 1.339 cm−1 debido a la presencia de sulfato de cobre pentahidratado en la reacción.
Figura 4: Espectro FTIR de la solución obtenida con el protocolo 5
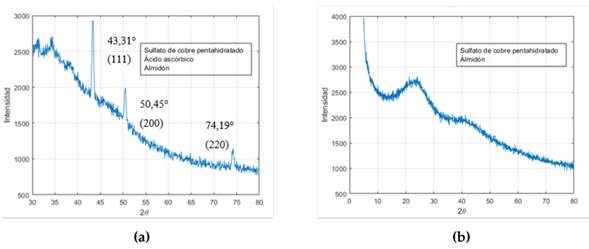
Según los resultados obtenidos al verificar la reproducibilidad de los métodos, solamente el protocolo 3 logró un resultado similar al reportado por 27, encontrándose un espectro de DRX similar y que representa el cobre metálico puro, identificado por lo picos en los ángulos 2θ de 43.31, 50.45 y 74.19°, que corresponden a la estructura cúbica centrada en las caras del cobre; así como a los planos (111), (200) y (220) respectivamente, lo cual concuerda con lo reportado por 27 y otros estudios 36, 37. Se concluye, entonces, que con este protocolo es posible obtener nanopartículas de cobre.
Figura 5: DRX de las nanopartículas de cobre sintetizadas con: (a) protocolo 3 y (b) protocolo 5
La Fig. 5b presenta el difractograma de la muestra obtenida con el protocolo 5. Se puede observar un pico ancho en 26° que no corresponde a lo reportado en la literatura para las NPs de cobre. Es posible que algunas macromoléculas presentes en el extracto de albahaca hayan enmascarado la superficie de las NPs de cobre, impidiendo su identificación en el DRX. 38 explicaron que esto se debe a la estructura cristalina dependiente de las características del polímero (peso molecular) y los parámetros utilizados en el proceso de síntesis y fabricación. Como resultado, este método también se descartó, ya que, aunque es probable que la síntesis de NPs de cobre haya sucedido, no es posible asegurarlo.
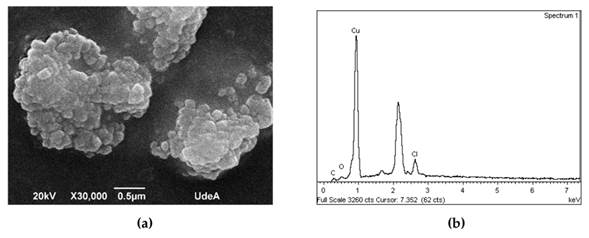
Mediante SEM, se obtuvo la Fig. 6a para la muestra sintetizada con el protocolo 3, en la cual se observan cúmulos de 2 µm, pues la muestra no se sonicó antes del ensayo. En la Fig. 6b, el análisis de EDS indica la presencia de cobre, carbono y oxígeno, que pueden atribuirse a los compuestos utilizados en la síntesis. También se observa cloro, que pudo haberse utilizado en la limpieza de la cristalería y/o los viales utilizados para almacenar las muestras.
Figura 6: Imágenes (a) SEM y (b) EDS de nanopartículas de cobre metálico sintetizadas con el protocolo 3
Según los reportes de la literatura, CuNPs de tamaños entre 2 y 5 nm han mostrado una actividad antibacteriana adecuada, al disminuir la concentración de microorganismos en un 99,9 % 39. Este tamaño corresponde a lo obtenido para los protocolos 3 y 5, y este hecho fue corroborado por 40, quienes evaluaron la actividad antibacteriana frente a E. coli empleando CuNPs de diámetro promedio de 4,8 y 7,8 nm. Estos autores encontraron que las NPs de menor tamaño exhibían una actividad antibacteriana significativamente mejor que las partículas más grande. Por su parte, 24 corroboraron la actividad antifúngica de CuNPs y CuONPs con un tamaño promedio entre 20 y 50 nm frente al hongo Fusarium sp.
Los resultados de la caracterización muestran que el protocolo 3 permite obtener NPs de 4,5 nm que podrían ser adecuadas para control biológico debido a su actividad antimicrobiana. Por otro lado, los análisis químicos evidenciaron la presencia de cobre y la fase presente de cobre metálico, el cual mejora la germinación y crecimiento de las plantas 41, por lo que las CuNPs podrían aplicarse también en cultivos.
Conclusiones
El protocolo 3, en el que se utilizó sulfato de cobre pentahidratado como sal precursora, ácido ascórbico como agente reductor y almidón como estabilizante, permitió obtener nanopartículas de cobre con un tamaño adecuado para un potencial uso en aplicaciones de control biológico.
La reproducibilidad de los protocolos que se pretendió replicar en este estudio no fue completamente verificada, ya que algunas condiciones de la síntesis y de la caracterización no se pudieron implementar. No obstante, adaptar los protocolos a las condiciones disponibles en el laboratorio permitió comparar las metodologías de obtención de CuNPs u CuONPs, así como analizar el efecto que las condiciones de síntesis tienen en sus características.
Acknowledgements
Agradecimientos
Al Comité para el Desarrollo e Investigación (CODI) por la financiación del proyecto de trabajo de grado identificado con el código PR21-1-06; al Grupo de Investigación en Biomateriales (Biomat); a Jorge Higuita-Castro y Sara Robledo-Restrepo del Programa de Estudio y Control de Enfermedades (PECET); y al profesor Luis Fernando Giraldo-Morales del Laboratorio de Investigación en Polímeros, por la colaboración brindada para el desarrollo del proyecto.
Referencias
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Daniela Acevedo-León, Claudia Patricia Ossa Orozco, Ana María Torres López

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
From the edition of the V23N3 of year 2018 forward, the Creative Commons License "Attribution-Non-Commercial - No Derivative Works " is changed to the following:
Attribution - Non-Commercial - Share the same: this license allows others to distribute, remix, retouch, and create from your work in a non-commercial way, as long as they give you credit and license their new creations under the same conditions.




2.jpg)